Significance of Movement and Exercise
Movement and exercise help an individual avoid chronic diseases. A good diet filled with nutrition and adequate regular exercise and movement impacts metabolism & physiology, boosts immunity, transfers higher oxygen levels to cells etc. Unfortunately, majority of us struggling to incorporate regular movement into our lives. Here in this blog, we discuss a combination of motivators for movement and exercise and strategies which can help an individual to navigate and build consistency for movement and exercise routine.
Inactivity and poor nutrition are two reasons for early mortality and other chronic diseases. More than 6% of people globally die due to physical inactivity. However, physical activity with good nutrition can help an individual stay healthy and avoid or even improve a wide range of chronic and non-chronic diseases. People are always finding shortcuts and quick fixes to stay healthy.
But every individual needs the right motivators for exercise and movement to follow and maintain a healthy lifestyle for a healthy body and mind.
Nutrition and Movement
Nutrition is essential for the human body. Without a properly planned diet, our body loses the nutrients to stay healthy and fit. But eating the right food alone can’t solve the problems of our body. The combination or integration of nutrition and movement helps our body maintain overall physical health.
Movement and physical exercise helps avoid and improve different diseases in the body. The two approaches are interdependent. For instance, movement or physical activity can’t fulfil nutrient deficiencies. Similarly, a good nutritious diet is not a substitute for physical activity. The body needs both nutrition and movement to stay healthy and fight diseases. The correct dosages of nutrition with significant motivators for movement and exercise will also help improve our overall lifestyle.
How Does Sedentary Lifestyle Affect our Health?
In the last few years, sedentary lifestyles have become a norm for the working class across the globe. A sedentary lifestyle is inevitable due to the increased desk jobs and excessive hours spent in front of the TV. Sitting for long hours can lead to chronic diseases and even early mortality.
Sitting is also a risk factor as it restricts oxygenation in the body. However, standing, walking, physical exercise, and other aerobic exercises contribute to better oxygenation in the body. Exercise also helps maintain redox balance. Movement can help an individual improve digestive functions and increase blood and lymphatic flow.
The Role of Movement and Exercise in Detoxification
Our bodies are exposed to thousands of chemicals every day. These chemicals enter our bodies from various channels and sources like body care products, cosmetics, air, water, fuel, plastic bottles and cleaning products. These chemicals enter our cells and eventually hinder and affect our hormones. Movement and Exercise Training helps detoxify our bodies from toxins and chemicals.
- Movement accelerates the process of sweating which in turn helps in throwing the toxins out of the body.
- Movement and Exercise is responsible for activating the lymphatic system. The active lymph nodes help filter toxins in the body and cleanse our system.
- It also helps increase the function of autophagosomes. This activity helps remove the old and useless cells in the body that can make our body more toxic.
- It is essential to maintain the levels of oxygen in the body are crucial. Physical exercise leads to increased oxygenation. Physical Exercise thus, in turn, circulates more oxygen in the blood.
- Undertraining and overtraining can lead to an imbalance of redox status in the body. Maintaining a redox level is necessary to avoid premature ageing and the risks of developing chronic diseases.
The Role of Oxygen, ATP production and Nitric Acid in the body
Our body intakes about 7.5 pounds of oxygen. About 3% of this oxygen intake ends up as free radicals in the body. Oxygen deprivation is a common phenomenon in the modern world due to a sedentary lifestyle. Boosting oxygen levels can thus help in boosting immunity and avoid the damage caused by ageing. Movement and Exercise Training helps in energy production and optimising oxygen levels in the body.
For instance, our body only uses 0,21 L of oxygen per minute while sitting. But brisk walking increases the use of oxygen levels up to 2.5 L of oxygen per minute. Exercising also contributes to the overall cardiac output of blood, increases the efficiency of the lungs in transporting oxygen and enhances the use of glucose in the cells and mitochondria.
Furthermore, our cells produce adenosine triphosphate(ATP), a crucial currency for energy in our body. The mitochondria need enough access to oxygen to boost ATP. Also, a good amount of nitric oxide makes the endothelial tissue softer and more flexible. This process thus enables an increased level of oxygen to reach the muscle cells and eventually the mitochondria. It further helps in the production of ATP in the body.
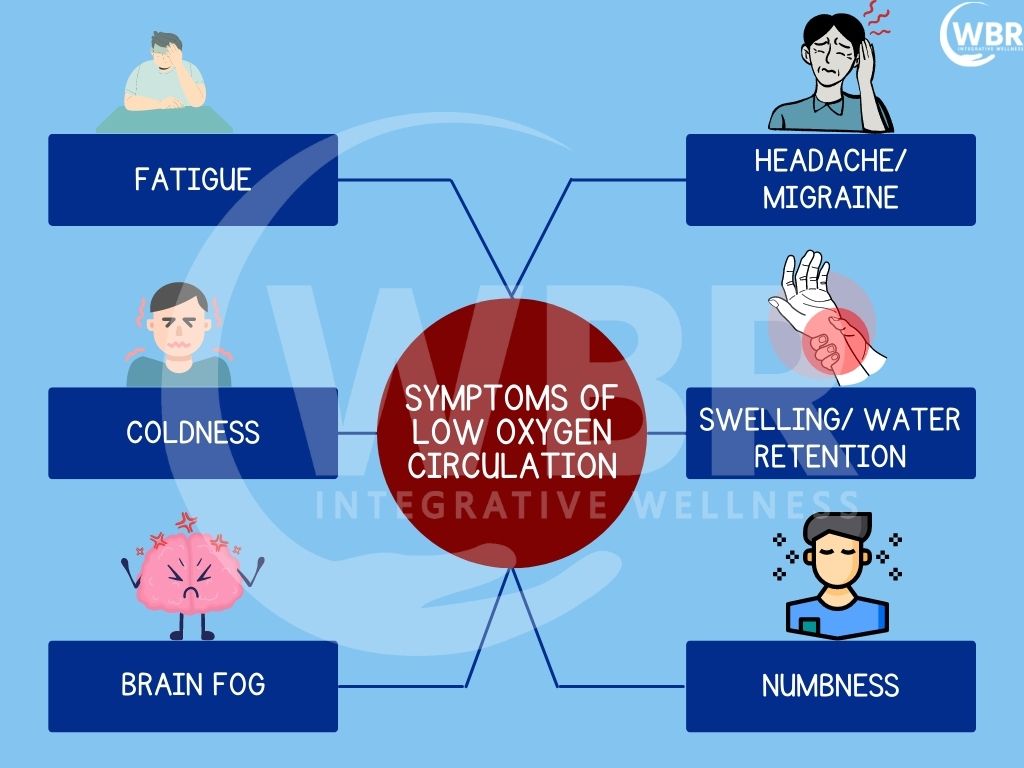
Symptoms associated with Poor Circulation of Oxygen
- Extreme Coldness in the body
- Brain Fog
- Poor Concentration
- Water retention and swelling in the ankles, neck or the upper arms
- Fatigue
- Numbness unrelated to a pinched nerve
- Headaches or migraines
Nutrients for Better Oxygen Circulation
Nutrients like citric acid or fumaric acid are essential to produce energy through the citric cycle in our body. Similarly, macronutrients, carbohydrates and amino acids are necessary to convert fuel in the body for the citric acid cycle. Oxygen is a vital element for all of these processes to function.
Here are some nutrients necessary for enhanced oxygen circulation in the body.
- Vitamin B and B12 are the primary contributors to producing red blood cells in the body.
- Iron is an essential nutrient for transferring nutrients and oxygen.
- Vitamin C is necessary for the utilisation of iron in the body.
- Vitamin K2 enhances the oxygen-carrying properties of the haemoglobin in the red blood cells.
- Magnesium improves the binding quality of oxygen and thus helps increase the flexibility of red blood cells to enter tiny spaces and capillaries in the body.
- Antioxidants in food items rich in phytochemicals, amino acids, vitamins and minerals help our body use oxygen more efficiently.
- Vitamin E is a leading element that helps transport oxygen to the red blood cells in the body.
Nutrients Items for ATP Production (Better Energy)
- Oxygen Levels in the blood
- CoQ10
- Vitamin B2
- NADH (Niacin Metabolite)
- Vitamin B5
- Vitamin B6
- Magnesium
Tips for Starters: Motivators for Movement and Exercise
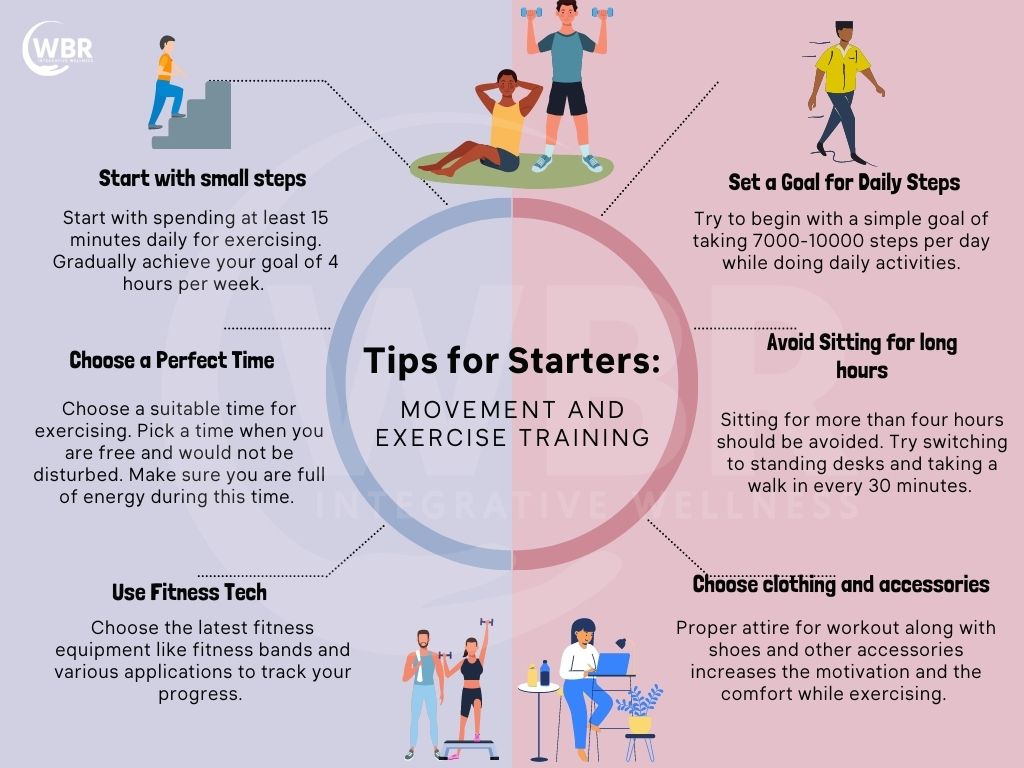
- Start with small steps. Exercise for 15 minutes initially and then gradually increase the duration of the workout. Make it a goal to reach 4 hours of exercising every week.
- Begin with a goal of 7,000-10,000 steps from everyday activities.
- Pick up a time when you have more energy to exercise.
- Do not spend more than 4 hours per day sitting. Working people can benefit from using a standing desk instead of a sitting desk.
- Many individuals try to work out in casual clothing and give up with ease initially due to discomfort. Choose proper workout attire, shoes and accessories. A suitable outfit for a workout will help increase your comfort and stick to a routine for a longer duration.
- People tend to stick to a workout routine when they have company. Try to build an exercise routine with your friends or find a local group that helps you achieve your goals.
- Gradually increase the Movement and Exercise Training dose every day. Get the necessary knowledge from experts before diving into a heavy physical routine.
- Make fitness bands and applications your best friend during your daily Movement and Exercise Training.
Movement and Exercise in a Busy Schedule
Most individuals work 40+ hours per week. After spending 8+ hours in offices and an additional 1-2 hours stuck in traffic, exercising becomes a far-fetched dream. But achieving physical fitness is essential. Thus, people with busy schedules can follow a routine to exercise daily. First, let’s understand what comprises physical fitness.
What is Physical Fitness?
Physical fitness is a broad term. But in simple words, we can focus on three areas to define physical fitness.
- Flexibility
- Strength
- Cardiovascular Health
The healthy fusion of these three in a body is considered physical fitness. Here’s how one can achieve physical fitness by dedicating merely 30 minutes daily to exercising.
- Warm-Up: 10 minutes
- Strength circuits: 20 minutes
- Interval Training: 5-10 minutes
Conclusion
Physical Exercise helps increase the oxygen level in the body. Inactivity and lack of movement during the day lead to higher risks of developing chronic diseases and early mortality. An integrative approach to nutrition and exercise can help an individual avoid chronic disease risk factors and maintain a healthy body and mind. A sedentary lifestyle and other factors are primary contributors to certain chronic diseases. Starting small and gradually achieving the training goal can help avoid and improve various physical and mental conditions. Starting with small motivators for movement and exercise can help individuals achieve the overall health goals.
References
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6027933/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4911341/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0092867414013178
https://bjsm.bmj.com/content/55/19/1099
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/21679169.2019.1623314









