Shield Your Pregnancy from Preeclampsia with a Functional Lens
What if preeclampsia, one of the most feared complications in pregnancy, could be prevented, not just managed?
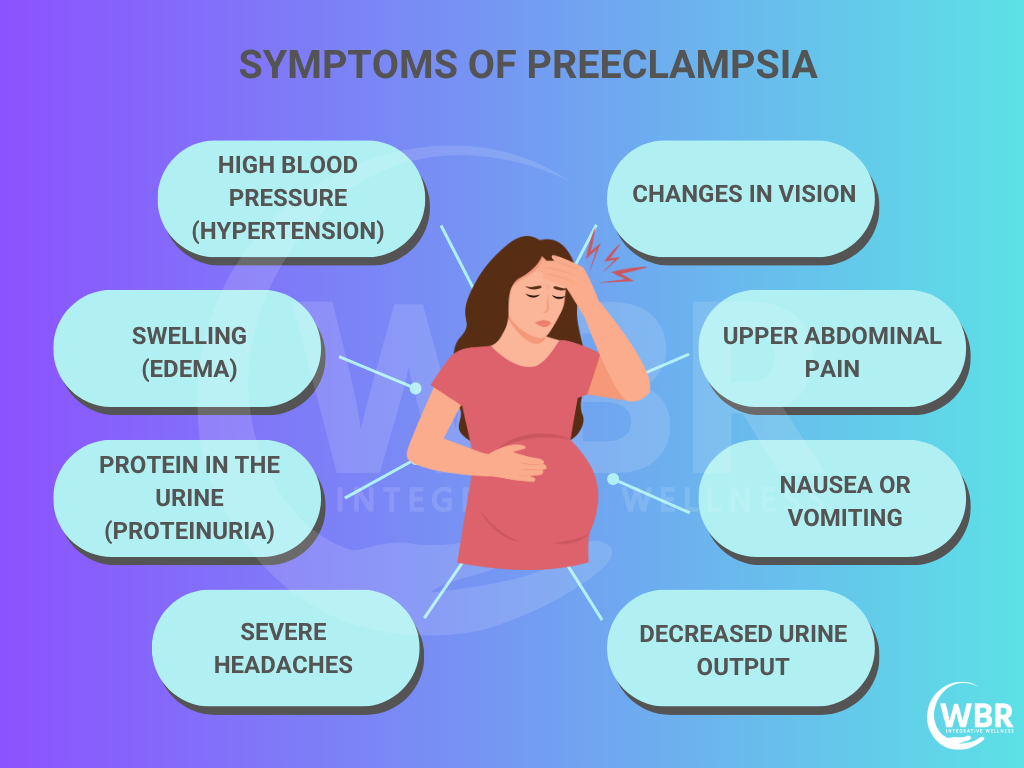
Preeclampsia affects up to 7% of all pregnancies, and it’s a leading cause of premature birth, low birth weight, and maternal death worldwide. It often shows up silently between the 20th week of pregnancy and in between 1-6 weeks after delivery, marked by rising blood pressure, protein in the urine, and swelling. But by the time symptoms appear, it is often too late.
Conventional medicine focuses on monitoring symptoms and intervening when complications arise. Integrating Functional Medicine along with a conventional approach makes a powerful difference and saves complications for both mother and child.
Preeclampsia, also known as toxaemia of pregnancy, is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition marked by high blood pressure and the presence of protein in the urine (proteinuria), often accompanied by swelling or oedema. It usually arises after the 20th week of pregnancy and extends into the first week postpartum. Moreover, it is a major contributor to maternal and infant complications, including premature birth, intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), and even perinatal mortality.
This placental disorder disrupts the blood flow between mother and baby, impairing nutrient and oxygen delivery, which results in low birth weight. Babies born to mothers with preeclampsia are four to five times more likely to experience health problems shortly after birth. Though early stages show few symptoms, the condition escalates quickly. If left untreated, it often leads to eclampsia, characterised by seizures, organ failure, and life-threatening complications for both mother and child.
By identifying root causes like nutrient deficiencies, oxidative stress, hormonal imbalance, and microbiome disruptions, Functional Medicine empowers women to take control from preconception to postpartum. Read along and explore evidence-based strategies to lower your risk of preeclampsia naturally, using targeted nutrition, specific probiotics strains, targeted supplements, functional lab testing, lifestyle tools, and more.
Reframing Preeclampsia Through the Functional Lens
Preeclampsia is often seen as a sudden, unpredictable complication but what if it’s actually the end result of deeper imbalances that begin long before symptoms appear? Functional Medicine shifts the focus to root cause analysis, helping us understand why preeclampsia develops in the first place.
Here are the key drivers from a functional perspective:
- Oxidative Stress: Damages cells, blood vessels, and the placenta.
- Endothelial Dysfunction: Impairs blood flow and raises blood pressure.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Low levels of magnesium, choline, and CoQ10 weaken maternal resilience.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Progesterone and thyroid issues impact placental health.
- Immune Dysregulation: Triggers inflammation and poor implantation.
- Microbiome Imbalance: Gut and vaginal flora shape immune response and metabolism.
Common Risk Factors leading to preeclampsia
Pre-eclampsia is not sudden; it develops on the foundation of some high-risk condition. Identifying these early warning signs is key to building a functional, preventative strategy.
Here are the most common risk factors:
- Age Extremes: Teen pregnancies and women over 40 face higher risks.
- History of Preeclampsia: A personal or family history significantly increases recurrence.
- Metabolic Syndrome: Includes insulin resistance, obesity, and high blood pressure all contributing to vascular stress.
- Hypothyroidism: Low thyroid function impairs hormone balance and blood pressure regulation.
- Chronic Infections: Silent infections disrupt immune tolerance and increase inflammation.
Knowing these risk factors helps guide early testing, targeted nutrition, and personalised support.
Evidence-Based Root-Cause Testing for Preeclampsia
Functional lab testing provides powerful insight into early imbalances that often lead to preeclampsia. Moreover, by evaluating specific biomarkers, it becomes easy to take proactive steps before symptoms emerge.
Here are essential markers to consider:
-
sFlt-1/PIGF Ratio (Soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1): A clinical biomarker for predicting preeclampsia risk. Elevated levels reflect anti-angiogenic activity, contributing to poor placental development and endothelial dysfunction.
-
Homocysteine: High levels are associated with vascular damage, oxidative stress, and impaired methylation, factors that increase preeclampsia risk.
-
Oxidative Stress Markers (e.g., 8-OHdG, MDA): Elevated markers suggest mitochondrial dysfunction and cellular injury, both of which are common in preeclamptic pregnancies.
-
Nutrient Status: Deficiencies in Vitamin D, Magnesium, Zinc, and Choline impair placental health and blood pressure regulation. Testing serum and RBC levels ensures accurate identification of functional deficiencies.
-
Inflammatory Markers (hs-CRP): Elevated levels point to chronic low-grade inflammation—a major driver of endothelial dysfunction and hypertension in pregnancy.
-
Thyroid Function (TSH, Free T3, Free T4): Subclinical hypothyroidism, even when TSH is within range, can increase the risk of preeclampsia. Testing FT3 and FT4 offers a more complete picture of active thyroid hormone availability.
-
Microbiome Mapping: Disruption in gut or vaginal microbiota, especially low levels of Lactobacillus crispatus, is linked to immune dysregulation and an increased risk of complications like preeclampsia and preterm birth.
- Urine Albumin Test: The urine albumin test detects protein in the urine, a key marker of preeclampsia. Levels above 300 mg/day suggest kidney stress due to high blood pressure, making it an essential tool for early diagnosis and timely intervention.
Testing these markers allows for personalised, targeted interventions, long before clinical symptoms develop.
Targeted Functional Nutritional Strategies
Functional nutrition focuses on using targeted nutrients to correct imbalances at the cellular and systems level. Here’s how specific compounds support the mitochondria, cardiovascular system, and immune health during pregnancy to reduce the risk of preeclampsia:
Mitochondrial & Endothelial Protection
- CoQ10 (150 mg BID): Boosts mitochondrial energy, protects blood vessels, and reduces oxidative stress.
- Alpha Lipoic Acid: Enhances insulin sensitivity and recycles antioxidants.
- Resveratrol + Quercetin + Curcumin: Potent anti-inflammatory blend that modulates oxidative pathways and vascular function.
Cardiovascular Regulation
- Magnesium + Taurine + Glycine: Promotes parasympathetic calm, lowers blood pressure, and improves vascular tone.
- L-Arginine: A nitric oxide precursor that supports vasodilation and healthy circulation.
- Calcium + CLA: In high-risk pregnancies, this combo has been shown to lower preeclampsia incidence by up to 78% through endothelial protection.
- Allicin: Allicin, a potent compound derived from garlic, supports healthy blood pressure during pregnancy. A daily dose of 180–540 mg helps prevent hypertensive spikes. Studies and anecdotal reports show it’s well-tolerated and effective, especially in women with a history of preeclampsia.
Methylation & Neurological Support
- Choline, B12, Methylfolate: Crucial for DNA methylation, fetal brain development, and reducing homocysteine.
- DHA & EPA (algae/fish oil): Supports fetal brain growth and maternal cardiovascular health.
These nutrient strategies not only reduce the physiological stressors behind preeclampsia but also enhance the mother’s and baby’s long-term health outcomes.
Note: Always consult a functional medicine practitioner and a medical practitioner to ensure supplement safety during pregnancy.
Iron for Preeclampsia
- Iron Deficiency & IV Iron in the Second Trimester
Iron deficiency, especially when ferritin levels are very low, compromises placental health and oxygen delivery, key factors in the development of preeclampsia. In such cases, intravenous (IV) iron during the second trimester is a safe and effective intervention to restore iron stores and reduce the risk of hypertension, proteinuria, and excessive weight gain due to oedema. - Supplement Options: Bisglycinate Chelate and Heme-Based Iron
Iron bisglycinate chelate is a gentle, highly absorbable form of iron that is less likely to cause gastrointestinal discomfort or constipation. When combined with cofactors like vitamin C, B6, B12, and folate, it enhances red blood cell production and supports vascular function. Alternatively, heme-based iron (e.g., Hemeboost Forte) offers superior bioavailability and is ideal for those with poor absorption.
Note: Always consult a functional medicine practitioner and a medical practitioner to ensure supplement safety during pregnancy.
Microbiome Restoration & Probiotic Therapy for Preeclampsia
The gut and vaginal microbiome are a powerful regulators of immune balance, metabolic health, and inflammation, key in preeclampsia prevention. Functional Medicine uses targeted probiotic and prebiotic therapies to nourish the microbiome and support maternal health from the inside out.
Targeted Probiotics
- LGG® (Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG) and BB-12® (Bifidobacterium animalis): Regulate glucose metabolism and reduce systemic inflammation.
- Lactobacillus crispatus: Dominant vaginal strain associated with reduced infections and improved pregnancy outcomes.
- S. boulardii CNCM-I-745: A beneficial yeast that strengthens gut lining, modulates immune activation, and lowers inflammatory markers.
Prebiotic Support for Preeclampsia
- PHGG (Partially Hydrolysed Guar Gum), Psyllium, FOS, and GOS: These are prebiotic fibres that nourish beneficial gut bacteria, enhance short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) production, and support gut barrier integrity. They help regulate blood sugar, reduce systemic inflammation, improve bowel regularity, and enhance mineral absorption, creating a balanced internal environment crucial for a healthy pregnancy.
Maintaining a healthy gut and vaginal microbiome lowers the risk of immune dysregulation, systemic inflammation, and metabolic stress, making it a critical pillar in functional preeclampsia prevention.
Natural Support for Cardiovascular Health in Preeclampsia
In preeclampsia, poor blood flow and vascular tension often puts both mother and baby at risk. Focus on boosting nitric oxide (NO), a key molecule that relaxes blood vessels, improves circulation, and supports healthy blood pressure. Here’s how to naturally enhance NO levels and protect vascular health:
- Add L-arginine-rich foods like pumpkin seeds, lentils, and turkey
- Include beets and beetroot juice to directly support nitric oxide production
- Use garlic and pomegranate for their vascular-protective and NO-boosting properties
- Load up on leafy greens (spinach, arugula, kale) for natural nitrates
- Supplement with Citrulline (with practitioner guidance) to sustain NO levels
- Take Vitamin C + E to reduce oxidative stress and support endothelial function
- Practice prenatal yoga or deep breathing to lower vascular tension
Together, these steps offer a safe, natural way to promote cardiovascular balance, reduce risk, and enhance placental blood flow in preeclamptic pregnancies.
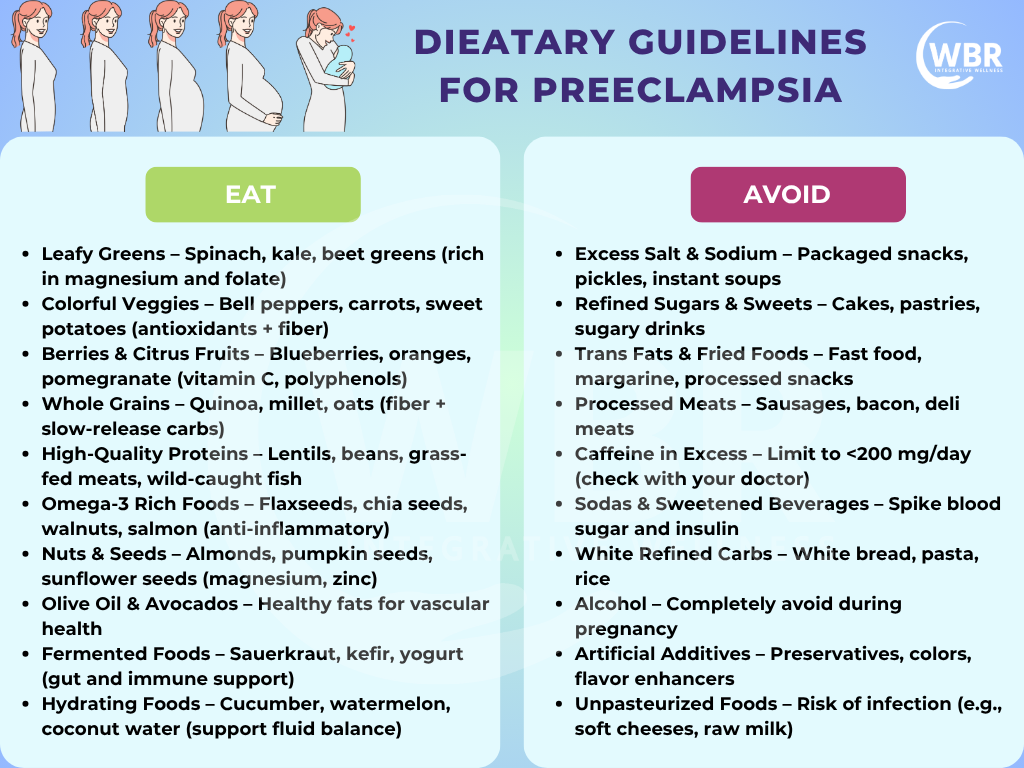
Dietary Guidelines for Preeclampsia
A nutrient-rich, anti-inflammatory diet plays a key role in lowering preeclampsia risk by improving blood pressure, supporting vascular function, and reducing oxidative stress. Here’s how to eat smartly and functionally during pregnancy
Choose Whole, Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Load your plate with vegetables, fruits, legumes, whole grains, seeds, and healthy fats.
Prioritise Low-Glycaemic Carbohydrates
Include oats, sweet potatoes, millet, and quinoa to regulate blood sugar and reduce insulin resistance.
Include Omega-3 Fats Daily
Get DHA/EPA from flaxseeds, chia, walnuts, or algae-based supplements to reduce inflammation.
Boost Magnesium & Calcium Intake
Eat leafy greens, sesame seeds, almonds, and plant-based milks to support blood pressure control.
Eat Protein with Every Meal
Aim for 75–100g/day from clean sources like lentils, tofu, eggs, or pasture-raised meat.
Stay Hydrated
Drink 2–3 liters of filtered water daily and use herbs like mint or lemon to support detox.
Support Natural Detoxification
Add beets, cruciferous veggies, and dandelion greens to your meals.
Limit Inflammatory Triggers
Avoid sugar, ultra-processed foods, trans fats, caffeine, and alcohol.
These small, daily choices can make a big difference in creating a safer, healthier pregnancy.
Functional Hormone Modulation with Progesterone
Hormonal imbalances, especially low progesterone, often play a central role in preeclampsia risk. Functional Medicine addresses this by supporting optimal hormone levels early in pregnancy.
Evidence-Based Insight
A recent meta-analysis reveals that vaginal progesterone supplementation before 20 weeks reduces the risk of:
- Preeclampsia by 36% (OR 0.64)
- Low birth weight (LBW) by 43% (OR 0.57)
Mechanism of Action
- Enhances uterine blood flow and placental perfusion
- Reduces vascular resistance
- Balances maternal immune tolerance for healthy implantation
Dydrogesterone
Especially useful in cases of recurrent miscarriage, dydrogesterone supports fetal growth and may improve pregnancy outcomes in women with luteal phase defects.
Progesterone therapy, when applied early and appropriately, becomes a powerful functional tool in lowering preeclampsia risk naturally.
Personalized Lifestyle Medicine
Lifestyle choices are powerful modifiers of preeclampsia risk. Functional Medicine emphasizes personalized, daily habits that support hormonal balance, immune function, and vascular health.
Exercise
Engage in moderate daily movement—like walking, swimming, or prenatal yoga to improve insulin sensitivity, enhance circulation, and reduce oxidative stress.
Stress Reduction
Chronic stress disrupts hormonal and immune balance. Incorporate yoga, breathwork, mindfulness, and nervous system support to lower cortisol and systemic inflammation.
Environmental Detox
Minimize exposure to heavy metals, pesticides, plastics, and VOCs by choosing clean food, water, and personal care products.
Anti-inflammatory Nutrition
Adopt a low-glycaemic, whole food diet abundant in plant-based polyphenols, omega-3s, fibre, and micronutrients to reduce inflammation and stabilise blood sugar.
Together, these lifestyle pillars form the foundation of a preventive and empowering approach to preeclampsia.
Preconception Optimisation for Both Partners
Preeclampsia prevention begins before conception. Functional Medicine emphasises optimising the health of both partners to support healthy implantation, placental development, and fetal growth.
Male Fertility Matters
- Supplement with CoQ10, antioxidants (like Vitamin C, E, and zinc) to improve sperm motility and mitochondrial function.
- Avoid testicular heat exposure from laptops, tight clothing, or excessive exercise.
Detox Before Conception
- Begin gentle detox protocols 3–6 months in advance using nutrients like glutathione, NAC, and liver support herbs to reduce environmental toxin burden.
Lifestyle Corrections
- Encourage balanced nutrition, stress management, and sleep hygiene in both partners.
- These changes improve epigenetic expression, support hormonal balance, and lay the groundwork for a healthy placenta and full-term pregnancy.
A healthy pregnancy starts with a healthy couple, well before the first positive test.
Postnatal Care & Recovery
The journey doesn’t end at delivery. Postnatal care is crucial for restoring balance, preventing complications, and supporting both mother and baby in the months that follow.
Nutritional Continuity During Lactation
Continue key nutrients like omega-3s (DHA/EPA), choline, and strain-specific probiotics to support milk quality, maternal brain health, and infant immune development.
Postpartum Reassessment
Regularly monitor thyroid function, iron status, and nutrient levels, as imbalances can persist or worsen after birth, affecting mood, energy, and healing.
Cardiovascular Recovery
Address lingering endothelial dysfunction and blood pressure concerns with ongoing support from magnesium, CLA, and anti-inflammatory polyphenols (like resveratrol, curcumin, and quercetin).
Functional postnatal care ensures deep recovery and builds a strong foundation for future pregnancies and long-term maternal health.
Conclusion
Preeclampsia doesn’t have to be a waiting game or a last-minute emergency. With the right tools and knowledge, it becomes something proactively prevented, not just reacted to.
Functional Medicine empowers women to act early, test deeper, and nourish smarter. By addressing root causes like oxidative stress, inflammation, nutrient deficiencies, and microbiome imbalances, we shift the focus from symptoms to solutions.
When you combine evidence-based supplementation, personalised lifestyle interventions, and preconception optimisation, you create a powerful and holistic strategy to protect both mother and baby naturally, safely, and effectively.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK570611/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5127661/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1521693424000270
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11972965/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9237898/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0140673620323357









