The Ultimate Guide to Low Histamine Diet
A low-histamine diet is one of several therapeutic diet to assist patients with food sensitivities, food intolerances, and/or food allergies. This diet is ideal for those who have some kind of histamine intolerance and suffer from various complications and symptoms such as like sneezing, hives, itching, flushing, migraines, profusely sweating, rapid heartbeat, fatigue, nose bleeding, car sickness, digestive issues, and more. Here in this blog we explore the root cause of high histamine and the diet to support the healing process.
What is Histamine?
Histamine, known as biogenic amine is a chemical found in our bodies. The Histamine chemical is released by the immune cells which are also known as the mast cells. This chemical is essential for the performance of the major systems of a human’s anatomy like the immune system, digestive system and neurological system.
The major function of Histamines is to fight allergens and repair physical injuries. When allergies and physical injuries occur, our brain directs the mast cells to release Histamine. The release of Histamine helps in flushing out the allergens. This process leads to an increase in blood flow to the affected area. This process can thus eventually trigger bodily issues like hives, sneezing and runny nose in certain individuals. But why does this happen? This occurs as certain individuals have Histamine Intolerance.
What is Histamine Intolerance?
A healthy body needs to break down the histamine level to maintain a healthy balance of the histamine chemical. The two main enzymes that help in breaking down histamine are called diamine oxidase (DOA) and histamine N-methyltransferase (HNMT).
Certain individuals experience an insufficiency of DOA and HNMT due to various reasons. The genetics, nutrient deficiency and a high intake of DOA and HNMT blocking substances lead to the insufficiency of these essential elements in the body.
Histamines are built in the body at a rapid rate as compared to their elimination process. The deficiency of histamine-breaking enzymes like DOA can lead to histamine intolerance. A histamine intolerant individual is not sensitive to Histamine but it simply means that an individual has developed an abnormal amount of histamine in his body.
Histamine builds up gradually in the body of an individual. A normal body will keep eliminating the histamine chemical with the help of enzymes like DOA. But an unhealthy body with histamine intolerance would not be able to maintain the normal levels of histamine. Some individuals experience the symptoms within a few minutes while the symptoms take a few days to show up in other cases.
The only way to manage histamine intolerance in an individual is to find the allergens that lead to these symptoms and follow a low histamine diet. There are certain food items with high histamine levels. Histamine intolerant individuals must avoid these edible items.
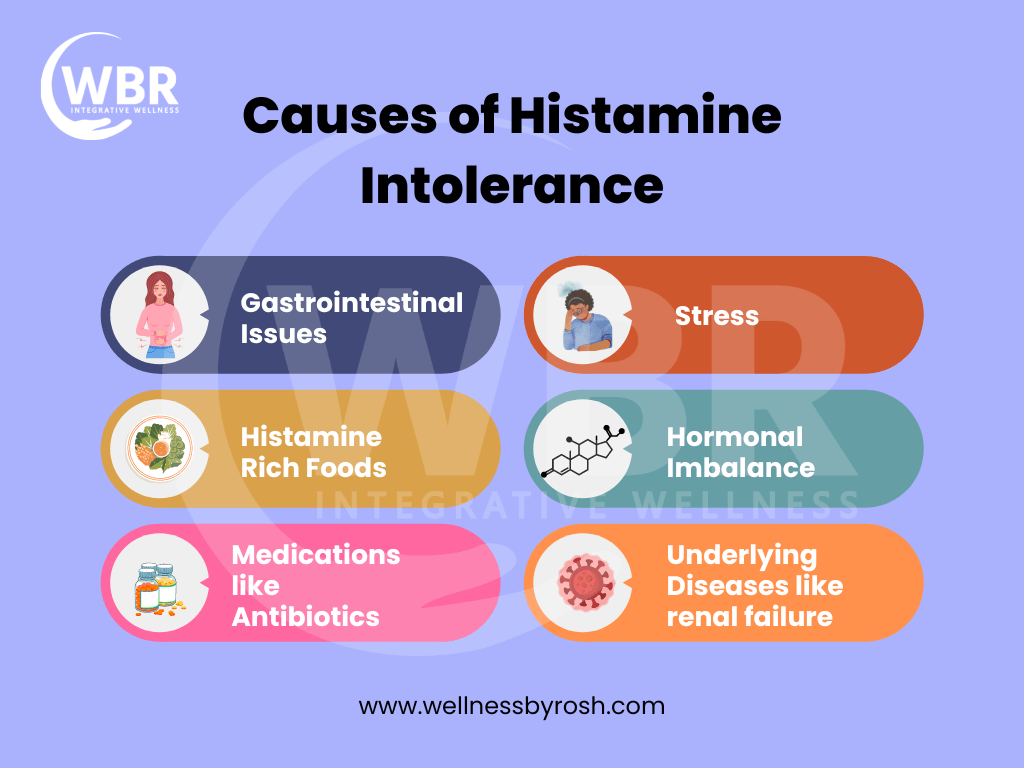
Causes of Histamine Intolerance
Histamine intolerance is actually an imbalance between histamine production and accumulation & ability of a body to degrade histamine. Releasing histamine is important for immune function. However if mucosal lining of the GUT is inflamed for any reason this can cause masts cells to become overactive. Here are some of the common causes that lead to histamine intolerance in individuals.
Gastrointestinal issues:
Various kinds of issues related to an individual’s gut can lead to histamine intolerance. Some of the common causes are gluten intolerance, SIBO/SIFO, irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel syndrome. These gut issues sometimes block the production of DOA in the body.
Stress:
The stress response may increase histamine production. Assisting clients with stress management is key in regulating histamine load.
Estrogen dominance:
Estrogens (both naturally occurring and estrogen- mimicking “xenoestrogens”) also contribute to the histamine load. Lifestyle and dietary interventions to reduce estrogen involve avoiding exposure to plastics or heating food in plastics.
Medications:
Certain medications like antibiotics can escalate the release of histamine by interfering with the histamine metabolism.
Lifestyle Disease:
Some chronic diseases are associated with histamine intolerance like fatty liver (NAFLD), thyroid autoimmune disease and some kind of kidney dysfunction.
What is a low-Histamine Diet?
The low-histamine diet is an elimination diet followed for the short term. The diet begins by eliminating the suspected food items that might be causing the allergy and leading to the increase of histamine levels in the body. Food items that are rich sources of histamine are also avoided under the dietary restrictions in a low histamine diet.
The diagnosis is made with the help of a physician or a certified dietician. Once the diagnosis is made and the allergens are ruled out, the diet must be strictly followed for a few months. During the low-histamine diet, food items affecting histamine levels and the food items rich in histamine are avoided by the individual suffering from histamine intolerance.
After the elimination phase, the suspected food items are slowly added back to the diet of the individual in small portions one at a time. This phase helps in checking the symptoms and the reaction of the body to these items. The allergy-causing foods and the triggers are then located with the help of this process during a low-histamine diet. During this diet, it is necessary to rule out the root cause behind histamine intolerance in an individual. For instance, a physician or a dietician needs to figure out whether a lack of DOA or a high histamine food item is the cause of the symptoms. Once this has been figured out, the individual can be kept on a specific diet based on the elimination of different food items.
Foods to Avoid and Foods to Eat
The freshness of a food item has a huge impact on the histamine levels. Leftovers and stale food items like fruits and vegetables that are not fresh, leftover dinner from the previous night and other such items with high microbial actions have high histamine levels. Such food must be avoided while following a low histamine diet.
Vegetables:
When dealing with vegetables in your diet, try to include fresh vegetables.
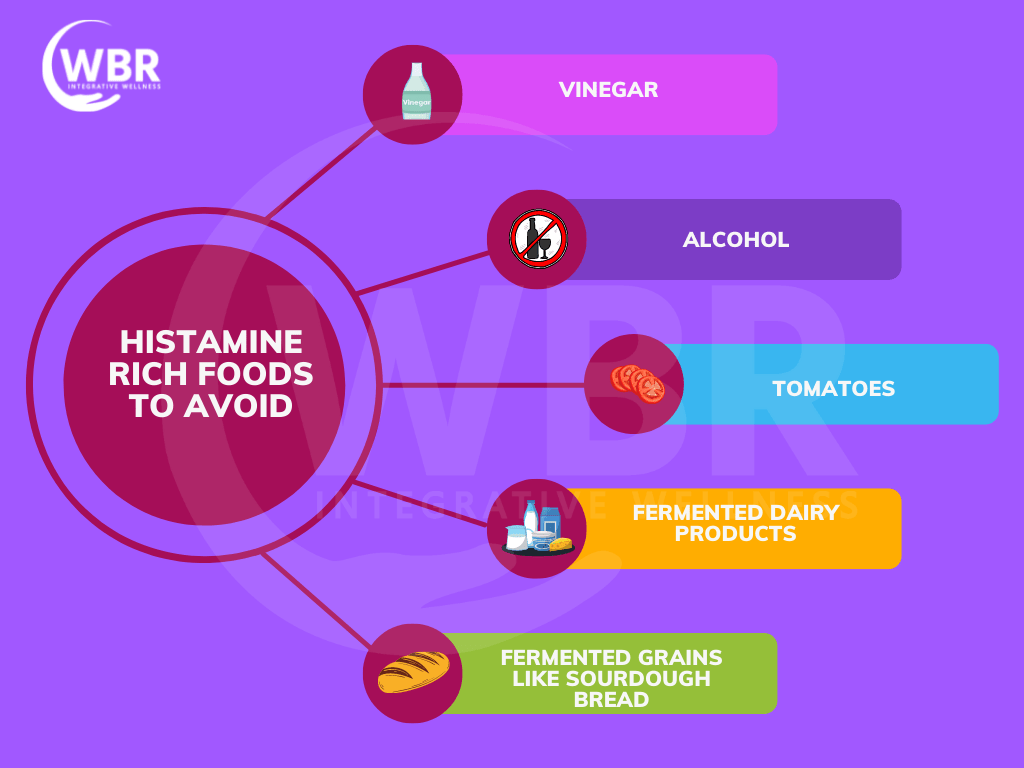
Avoid: eggplants, green brands, fermented vegetables, mushrooms, olives, peas, spinach, tomatoes and tomato-based products.
Fruits:
Fruits that are fresh are good to consume as long as they are not high in histamine or causing any kind of allergy
Avoid: avocados, bananas, guava, kiwi, papaya, pears, pineapples, plums, raspberries, strawberries, and dried and over ripe fruits.
Bakery Items
Avoid: pastries, pastry and dough mixes, sourdough bread, wheat germs and yeast bread.
Protein-rich foods
Food items rich in proteins like egg yolks, chestnuts, macadamia nuts, fresh-caught fish, frozen meat and fish and fresh-cooked meats can be consumed while following a low-histamine diet.
Avoid: almonds, bacon, beans and lentils, beef, canned, cured, dried, dry-cured, marinated, and smoked meats or fish; cashews; collagen; egg whites; finely chopped or ground meats (meatloaf, meat spreads); fish (anchovies, herring, mackerel, mahi-mahi, sardines, tuna), fish sauce; gelatin; liver; peanuts; sausage; shellfish; soy (tofu, tempeh); venison; and walnuts
Dairy
Fresh dairy products and unripen cheese like mozzarella and ricotta can be consumed.
Avoid: aged cheese, buttermilk, kefir, and processed cheese.
Spices/Flavoring
Most spices are fine to consume as long as they are fresh and low in histamine levels.
Avoid: anise, cayenne, cinnamon, cloves, flavor enhancers like glutamate, nutmeg, fish sauce, soy sauce and vinegar.
Beverages
Fresh beverages like almond milk, coconut milk, fruit juices from tolerated fruits and herbal teas are fine for consumption.
Avoid: black tea, green tea, alcohol, kombucha, energy drinks, soy milk and tomato juice.
Sweeteners
Natural sweeteners like honey, sugar and unprocessed jam from tolerated fruits can be consumed.
Avoid: cocoa and vanilla extract.
It is important to note here that the list of items to be avoided and to be consumed may vary for every individual. The list can be prepared by contacting a certified dietician, physician or practitioner. After a proper diagnosis one can make out what is to be avoided and what is consumable for an individual suffering from histamine intolerance.
Tips to follow while staying on a low histamine diet
- Avoid eating leftovers. Freeze fresh food and consume it as soon as possible.
- Manage histamine levels with the help of nutrients and supplements that support decreasing histamine levels like selenium, quercetin, Vitamin C, B12, zinc, EGCG, DOA and stinging nettle.
- Keep stress levels in check by following effective stress management techniques.
- Check for gut inflammation/SIBO and get the support needed to manage it.
- Limit the consumption of high histamine foods like red wine, champagne, aged cheese, cured meat and fish, vinegar and fermented food items and stick to the dietary plan suggested by your nutritionist or physician.
- Specific probiotic strains (microbes) can assist with histamine degradation such as Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, and Bifidobacterium longum, Lactobacillus gasseri (BNR17), Lactobacillus Reuteri, B. Coagulans. Avoid probiotic species such as Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus bulgaricus as they add to histamine production.
FAQs
- It takes three to four weeks to get rid of histamine intolerance symptoms. Most patients show results in about three weeks of following a low-histamine diet.
- The best way to treat histamine intolerance symptoms is to start an elimination diet. Avoiding histamine-rich foods and triggering food items is the way to deal with histamine intolerance.
- A blood test to check the DOA levels in your blood can be the first step to diagnosing the problem. This test helps in locating the cause of certain histamine-related symptoms.
- Some of the most common symptoms related to histamine intolerance are headaches, bloating, nausea, dizziness and flushing of the head and chest.
- Excluding similar conditions like celiac disease, irritable bowel syndrome and lactose intolerance helps physicians in ruling out the occurrence of histamine intolerance in an individual.
- In case if you are on antihistamine prescription then this can decrease stomach acid as well as vitamin B12.
Conclusion
The low-histamine diet is a short term elimination diet to support histamine intolerance individuals which can be for few weeks or month. While following the low-histamine diet it is important to investigate the actual root cause of the histamine intolerance which can be like SIBO, fatty liver, inflammation, toxicity overload etc. It is crucial for histamine intolerant people to follow a diet prescribed by a professional dietician or a physician as per the requirements.
References
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8308327/
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2018.01873/full
https://www.jandonline.org/article/S2212-2672(14)01454-3/fulltext
https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/85/5/1185/4633007










Deepmanyu
21-Jun-22Knowledge is really Nice.
Aruna Tewani
21-Jun-22This is amazing information for people who are struggling with food allergies and intolerances; I believe everyone should read this article and it will help them so much. Roshan puts so much research in every health issue he writes about, his articles are so comprehensive and they are all a must read – there’s something in there for everyone! Roshan is already an amazing health coach and I cannot wait for him to become a certified functional doctor because I know he will be one of the best!