Coenzyme-Q10: An Crucial Supplement for Hypertension, Metabolic Syndrome and Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Coenzyme-Q10 is also known as CoQ10 is a fat soluble antioxidant vitamin that plays an indispensable role in intracellular energy production. This can be made by the body itself from tyrosine or can be taken from the dietary sources as its production decreases with the age. As per recent studies, CoQ10 is a powerful antioxidant and safely used in supplement form for a wide range of diseases. CoQ10 showed various health benefits, such as in heart health, preventing migraine, insulin resistance, mitochondrial dysfunction etc. In this blog, you’ll get to know more about CoQ10, its uses, benefits, side effects, dosage and other top facts about this crucial cofactor for the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
What Is Coenzyme-Q10?
Coenzyme is a fat-soluble vitamin-like element that is synthesized in our body and stored in the mitochondria of our cells. As we know that mitochondria produce energy, protect cells from oxidative stress and pathogenic bacteria and viruses. Coenzyme-Q is found naturally in every cell of our body and is also present in many food items. It is a powerful antioxidant that provides protection from toxic free radicals and prevents aging-related cellular damage. The production of ATP requires coenzyme Q10 as it is an essential component in the transfer of electrons from chemical bonds in food molecules to chemical bonds in ATP molecules.
Different Forms Of CoQ10
There are 2 main types of Coenzyme Q10:
- Ubiquinone (CoQ10)
- Ubiquinol (CoQ H)
Ubiquinone: It is the active antioxidant form of CoQ10. Ubiquinone is mostly present in dietary supplements, that’s why it is considered a cost-effective form of CoQ10.
Ubiquinol: It is an oxidized form of Coenzyme Q and its function is associated with the metabolic chemical reactions that generate energy and most benefit as an anti-aging process. CoQH is harder to find in natural supplements, that’s why considered expensive.
Natural Food Sources Of CoQ10
Coenzyme-Q10 is naturally present in our food both vegetarian food and non-vegetarian food. Some major food sources of CoQ10 includes:
Vegetarian Sources:
Fruits: Strawberries, Oranges
Vegetables: Broccoli, Cauliflower and Spinach
Legumes: Soybeans, Lentils and, Peanuts
Nuts & Seeds: Pistachios and Sesame seeds
Oils: Canola Oil and Soybean oil
Tea: Arjun Tea (Arjun bark tea)
Non-vegetarian Sources:
Fatty Fish: Sardine, Trout and Herring
Muscle Meat: Chicken and Pork
Meat Organ: Liver, Heart and Kidney
Health Benefits Of CoQ10
Coenzyme-Q10 plays various roles in our body. The main crucial function is to help in energy production in the cells. Research suggests that CoQ10 causes many health benefits including:
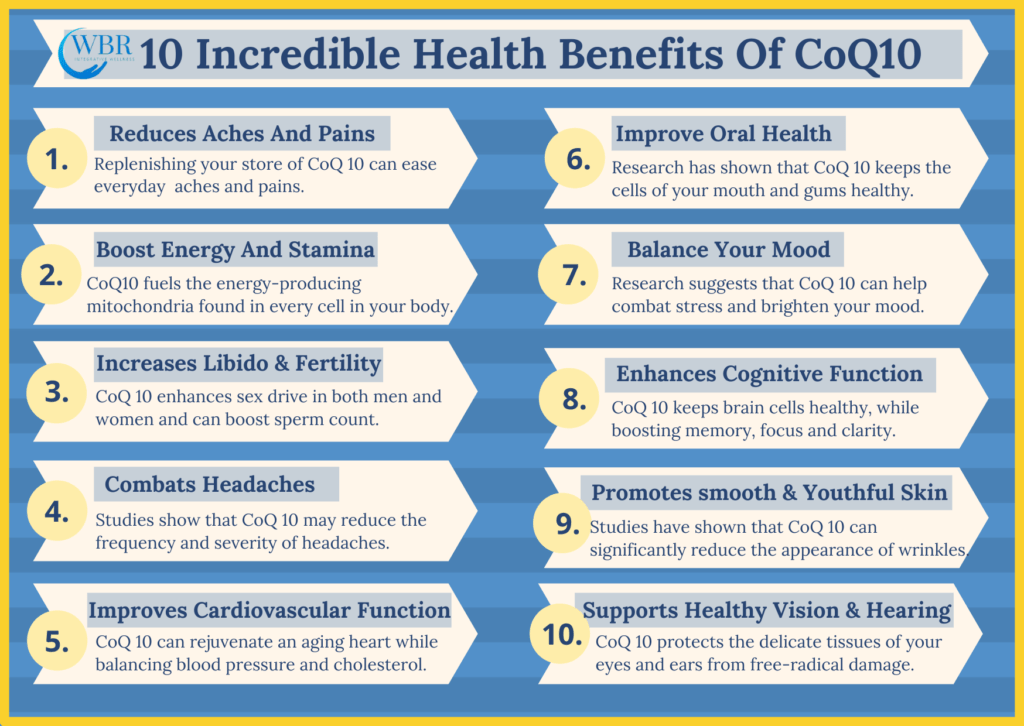
1. Cardiovascular Health
The effect of CoQ10 can reduce two significant drivers of hypertension, oxidative stress and hyperinsulinemia, improving cholesterol values and peripheral vascular resistance. Can help in the reduction of systolic and diastolic blood pressure by 10-16%.
2. CoQ10 Help In Diabetes
Oxidative stress can cause cell damage and that may lead to develop metabolic diseases such as diabetes. CoQ10 increases insulin sensitivity and help in blood sugar regulation.
3. Boost Energy And Increases Stamina
CoQ10 is involved in ATP production in energy pathway, low level of CoQ10 can be directly decreased our energy and lower our stamina.
4. Lowers Migraine
Migraine are severe headache that can lead a person feeling completely troubled. It has been shown that the CoQ10 help reduces the migraine.
5. Keep Your Skin Young and Smooth
Some internal factors, such as hormonal imbalance and cellular damage and external factors, like pollution, UV rays are hazardous elements and may cause skin damage. CoQ10 directly applying to the skin can reduce the damage of skin cell and protect from antioxidants, as a result skin become smooth and flawless.
6. Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease, a chronic disorder that primarily affects the middle-aged and old, but may also attack younger aged also. As we mentioned that CoQ10 production, reduces with age and so the cellular energy. Recent studies uncovered the whole new role of CoQ10 in Parkinson’s treatment, It magically helps in reversing mitochondrial dysfunction and plays an important role as a powerful antioxidant.
7. It May Improve Exercise Performance
Muscle function may get affected by oxidative stress. CoQ10 help in reducing oxidative stress and support mitochondrial functions and increase the energy level during exercise.
Supplement Of CoQ10
Generally in early age, you can avoid CoQ10 supplementation and complete your daily intake through dietary food, however, after the age of 50 the production of CoQ10 is decreased significantly, since it help in anti-aging process you can start CoQ10 supplements.
If you use supplements, make sure to take it with fat source, as CoQ10 is a fat-soluble substance.
Dosage Of CoQ10
The recommended dosage is 100-200 mg/day post meal with some fat.
Note: Kindly consult your medical practitioners before taking any supplements.
Important FAQ’s
- Always consume CoQ10 supplement with a meal as it is a fat-soluble nutrient and best absorbed when taken with the diet.
- To get added antioxidant benefits, take a CoQ10 supplement with antioxidant-rich food like herbs, vegetables, and spices.
- CoQ10 is needed to produce ATP, B1, B2, B3, B5, and antioxidants.
- Check HDL (good cholesterol) level because it has been seen when CoQ10 level is low, HDL is also low in many cases.
- Consuming CoQ10 with vitamin K may increase the risk of blood clotting.
- To check Coenzyme-Q10 levels in the blood, HPLC (high-pressure liquid chromatography) is considered the standard test.
- People who have a deficiency in CoQ10 levels often experience physical fatigue and muscle weakness.
- CoQ10 may interact with some medications, like warfarin and HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, and impact the drug effect.
- Coenzyme Q10 reduces inflammation, is a potent anti-oxidant, and is the first line of defense against low-density lipoprotein (LDL) oxidation.
- Some studies suggest that CoQ10 can improve fertility in both females as well as in males.
- Fatigue and exercise intolerance should respond well to supplementation of CoQ10.
- Is the patient on prescription drugs such as statins, antacids, or corticosteroids? If so, they might benefit from supplementation of CoQ10 and B12 respectively.
- CoQ10 levels are significantly lower in those with COPD, asthma, and other lungs issues.
- It is safe to be used at a dosage of 100-200 mg for pregnancy use in preeclampsia during the final trimester.
- Side effects are not infrequent but include abdominal discomfort, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, rash, and headache, especially on high dosages like > 600 mg per day.
Conclusion
To sum up, Coenzyme-Q10 is a fat soluble antioxidant that has many health benefits. Its main function is the production of cellular energy and preserving cells to slower the aging. Studies have shown that CoQ10 is also improves heart health, prevent cancer, lowers the headache and migraine. It also lowers the oxidative stress and prevent from toxic free radicals.
People of all ages can be benefitted from CoQ10, especially adults above 50 age as it decreases the ageing. It is a safe and non toxic supplement which is likely to be safe in pregnancy as well. Whenever you start a CoQ10 supplement, first talk to your health care provider and immediately stop if you feel any kind of discomfort or side effect.