Iodine Role in Metabolic and Cognitive Health
Iodine is an essential trace element that is required for the proper functioning of the thyroid gland in the body. Iodine deficiency often leads to the enlargement of the thyroid gland, hypothyroidism, metabolic disorder, poor school performance, slow growth, and cognitive disabilities in children. It plays role of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial effects on all these organs that have a concentration function. This includes thyroid, stomach mucosa, salivary glands, breast tissue, thymus, skin, placenta, ovaries, uterus, prostate, pancreas, choroid plexus, and the ciliary body of the eye.
Iodine deficiency can be diagnosed and treated with the help of an iodine-rich diet or natural supplements such as kelp.
Iodine Role and its Main Action
The thyroid gland is an essential part of the human anatomy. It regulates growth, metabolism and various other functions of the human body. Iodine is one element that is responsible for the production and proper functioning of the thyroid gland. As Iodine is not naturally available in our body, we depend on various food sources for iodine. Iodine is consumed by humans in the form of iodide salts which are found in sea salt, seawater fish and certain kinds of vegetables that are more bioavailable.
Iodide from such food items is constantly sent to the small intestine after consumption. It is then distributed through the blood to different tissues in our body. The thyroid gland absorbs more than 80% of the iodine in our body.
Iodine is necessary for producing T4 and T3. These hormones are essential for the growth, maturity and oxidation of the CNS. They also enable the metabolism of various tissues in the human body. The thyroid hormones like T3 cling to the nuclear receptors present on the surfaces of the cells. This in turn helps in the binding of zinc fingers in the receptor protein to the DNA.
Clinical Use and Benefits of Optimal Iodine
The adequate intake of iodine is critical for human health beside healthy thyroid function. Here are some of the benefits of consuming an optimal amount of iodine in the diet.
-
Thyroid Health
Iodine is responsible for the production and functioning of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland, located in the lower front part of your neck is responsible for the metabolism, hormone production and various other functions of the body. Proper iodine intake helps in promoting thyroid health.
-
Reducing the Risks of Goitre
The thyroid gland enlarges and forms goitre as a direct result of iodine deficiency. Iodine deficiency can often lead to hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. The goitre formed due to iodine deficiency can be easily reversed by increasing iodine consumption in the diet.
-
Treating Thyroid Cancer
Cancerous thyroid cells can be destroyed with the help of radioiodine. Many patients are found to be treated for thyroid cancer by orally consuming radioiodine radioactive iodine medications.
-
Brain Development during Pregnancy
Sufficient iodine intake during pregnancy is directly linked to the neurodevelopment of the child in the womb. Iron deficiency during pregnancy, on the other hand, can lead to lower IQ levels and cognitive disabilities in the early years. The recommended iodine intake for pregnant women is 220 mcg per day. While a normal adult is recommended to consume 150 mcg per day.
-
Prevention of ADHD
Adequate intake of iodine (approx. 250 mcg/day) may prevent maternal deficiency of iodine which can reduces the chance of developing ADHD later in newborn.
-
Cognitive decline in Children and Adolescents
Iodine deficiency in children and adolescents may result in poor school performance, higher incidence of learning disabilities, reduced mean IQ scores. Adequate iodine can help in partial reversal of cognitive impairment.
-
Treatment for Fibrocystic Breast Disease and Breast Cancer Prevention
Iodine supplementations helps for case of pain and fibrosis for women with fibrocystic breast disease. Also low free T4 was a risk for the development of breast cancer so optimal iodine level can have protective effect against breast cancer.
-
Treatment for Infections
The bacteria around cuts and wounds can be killed by applying iodine. Iodine in the liquid form can be used around cuts and wounds. Applying liquid iodine around injuries provides relief to such wounds. Bu cuts and wounds of children should not be treated with topical iodine application.
Causes of Deficiency
Iodine deficiency can be traced in certain groups of individuals. Various factors contribute to iodine deficiency around the world. Here are some of the common causes and groups that are at a higher risk of developing iodine deficiency.
-
Strict Diets
Strict diets with elimination can cause iodine deficiency in certain individuals. If a person is following a diet that eliminates all the dietary sources of iodine like dairy products, iodized salts, grains and certain iodine-rich vegetable oils, then they are more prone to developing iodine deficiency.
-
Hypertension
Patients suffering from heart disease, hypertension or high blood pressure are more prone to developing iodine deficiency. Such patients are advised to decrease their salt intake. In such cases, they tend to develop iodine deficiency and related complications.
-
Other Nutrient Deficiencies
Other nutrient deficiencies can also lead to iodine deficiency in the body. For instance, deficiency of nutrients like iron, selenium, zinc and even Vitamin A can be associated with the development of iodine deficiency and its related symptoms.
-
Goitrogens Rich Foods
Goitrogens are elements that are present in certain kinds of dietary items. These substances are responsible for blocking iodine from reaching the thyroid gland. Some of the food items rich in goitrogens are cabbage, broccoli, kale, cauliflower brussels sprouts, turnips, linseed, millet, soybean, and soy. Separating intake of iodine rich food from goitrogens food can improve iodine utilisation. Also soy consumptions for the case of thyroid medications can increase dosage requirements for thyroid supplementation.
-
Pregnant and Nursing Women
Pregnant women need more iodine as it contributes to developing the foetus and the growth of the baby’s brain and body. Pregnant women are thus more prone to developing iodine deficiency if the daily required amount of iodine is not consumed. Pregnant women should consume at least 220 mcg of iodine per day. While nursing women are recommended to consume 290 mcg of iodine every day.
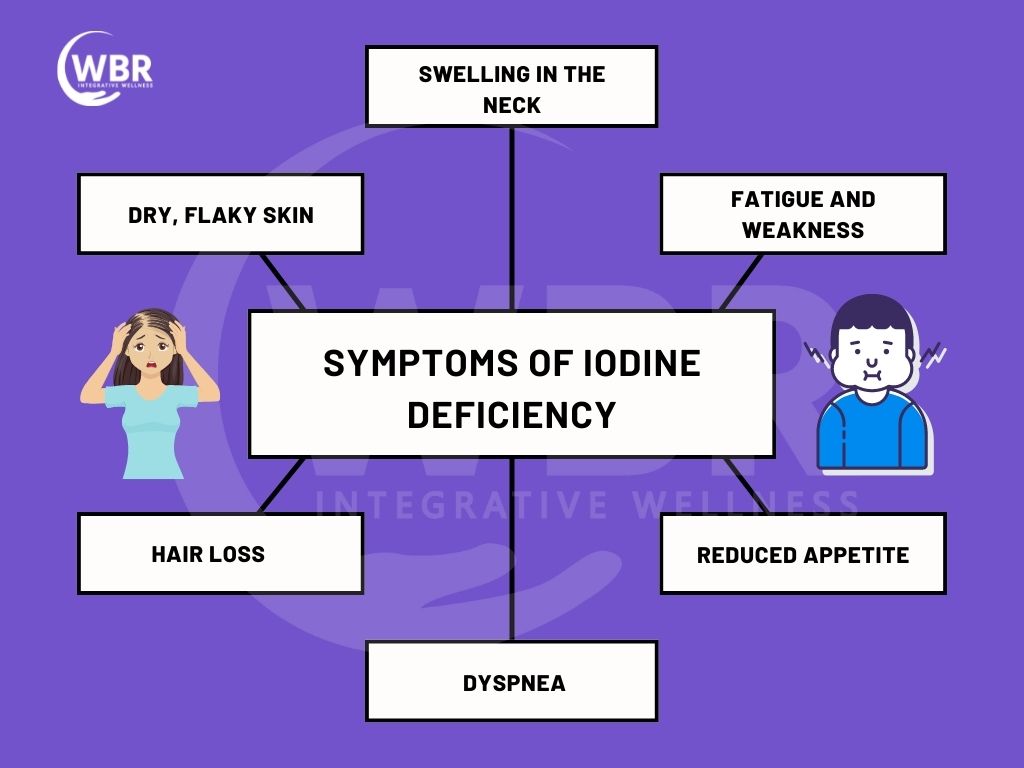
Signs and Symptoms of Iodine Deficiency
The regular iodine levels in the body are checked with the help of urinary iodine concentration. If the urinary concentration of iodine ranges between 100-200 micrograms, then it is considered a case of MUIC or Medium Urinary Iodine Concentration. Urinary Iodine concentration between 50-100 micrograms is termed mild iodine deficiency. The concentration of iodine in urine between 29-49 micrograms is considered a moderate deficiency. While severe iodine deficiency is diagnosed when the urinary iodine concentration is less than 20 micrograms. Here are some of the common signs and symptoms of iodine deficiency.
- Swelling in the neck
- Unexpected Weight Gain
- Fatigue and weakness
- Dry, Flaky Skin
- Colder body temperature and sensitivity to coldness
- Fluctuating Heart Rate
- Trouble Remembering Things or Cognitive Imbalance
- Heavy Menstrual Cycles
- Hair Loss
- Complications during pregnancy
- Dyspnea
- Reduced Appetite
- Constipation
Integrative Diet Approach to Boost Iodine/ Food Sources
Our body does not produce iodine naturally. Also, there are very few natural sources of iodine available in nature. Every adult must consume 300-400 micrograms of iodine per day for optimal health. Here are some of the dietary items that are rich in iodine and can help in boosting the iodine levels in the body.
- Seaweeds : Nori, Kelp, Kombu, Wakame
- Iodized salts
- Dairy products like milk
- Prunes in the dried form
- Sea vegetables
- Spirulina and chlorella
- Baked potato with skin
- Cranberries
- Navy beans
- Wild caught fish, shrimp, chicken

FAQs
- Iodine deficiency can be diagnosed with the help of various clinical tests like blood test and urinary iodine concentration (UIC).
- Iodine and thyroid optimisation enhances the skin moisture.
- Optimal level of Iodine and thyroid health can helps to lower the lipoprotein(a) because of genetic variant.
- Restoring optimal level of Iodine and thyroid health helps to reduce constipation.
- Iodine is capable of inducing apoptosis in human breast cancer cells through mitochondrial-mediated pathways..
- Iodine deficiency can lead to mental disabilities and lower IQ levels in children if the pregnant or nursing mother has iodine deficiency.
- Restoration of iodine optimal level usually develops over 2-3 months with gradual relief from hypothyroid symptoms (but only if iodine deficiency is the primary cause)
- Important to limit the exposure to the halogens consisting of fluoride, chlorine, and bromine. Iodine is a halogen as well, and excessive exposure to fluoride, chlorine, and bromine may result in the thyroid absorbing and storing these halogens, and thus displacing iodine.
- Low selenium dietary intake can exacerbates the effects of iodine deficiency as selenium deficiency results in decreased T4 catabolism which can leads to increase production of peroxide and thyroid cell destruction.
Supplements Guidelines
- Dosage for adults : 200 to 500 mcg (micrograms) per day
- Dosage for kids : 50 to 120 mcg (micrograms) per day ( Age 1 to 12 years)
- The daily dose is micrograms (µg, mcg) of elemental iodine, and not the total weight of the iodine compounds consumed.
- Supplement best options are kelp tablets, kelp flakes, potassium iodide liquid drops.
- Avoid preparations like Lugol’s or Iodoral form as that is high concentration dose may result in toxicity.
- As iodine is antimicrobial in nature so probiotics/fermented foods to be taken at different time separated by 2-4 hours.
- Selenium is companion mineral for iodine which helps in T4 to active T3 hormone. Taking 1-2 Brazil nuts daily meet the daily requirement of 200 mcg.
- Caution for autoimmune thyroid cases (Hashimoto’s thyroiditis) to avoid iodine supplements until antibodies test are negative as it causes cytokine and chemokine mediated lymphocyte infiltration which can damage thyroid further.
-
Weakness/dizziness may be a side effect of iodine supplementation primarily due to a hyperthyroid reaction due to either an autoimmune thyroid condition or activation of an abnormal nodule.
Conclusion
Iodine is an essential nutrient that is becoming increasingly deficient in modern people, especially those who live away from coastal ocean regions. Iodine is essential for the proper functioning of the thyroid gland, for normal growth and development and for protection from cystic breast disease. Iodine deficiency can cause various complications like the enlargement of the thyroid gland(goitre), hypothyroidism, oxidation, slow growth and other metabolic disorder. The deficiency of iodine in the body can be corrected with the help of dietary changes and supplements. Taking kelp flakes regularly can support in maintaining optimal iodine levels if deficient.
References
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3074887/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6145226/
https://pmj.bmj.com/content/77/906/217
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0308814621023359
https://www.bmj.com/content/352/bmj.i941/rr-2
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/0021968161900133