Key Nutritional Supplements For Chronic Kidney Disease
Are you getting the proper nutritional support to manage your symptoms and stage of Chronic Kidney Disease? Chronic Kidney Disease leads to a gradual loss of kidney function over time. Managing Kidney Disease requires a comprehensive approach that includes medication, lifestyle changes, and particularly, nutritional supplements. Proper nutrition significantly impacts the progression of CKD and the quality of life of those affected. In this blog, we delve into key nutritional supplements beneficial for CKD patients and when and how to use them.
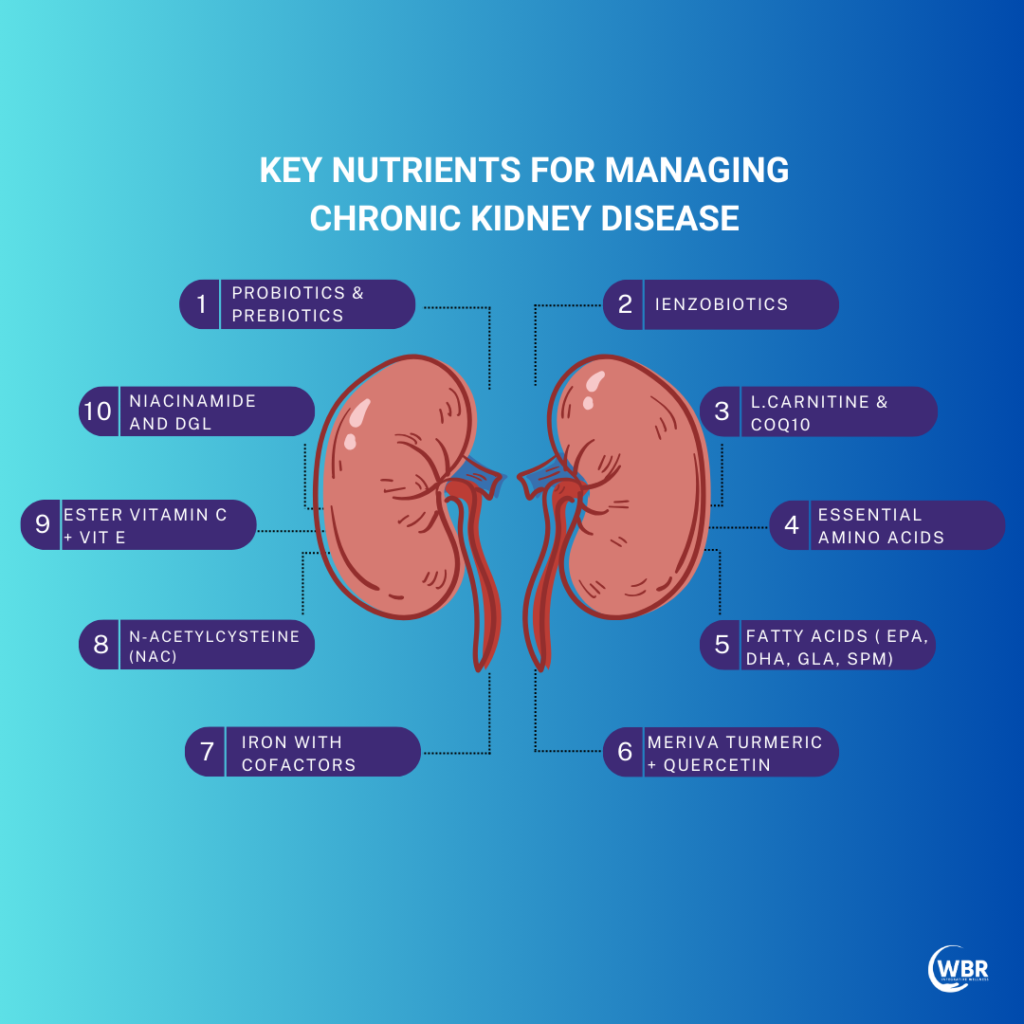
Enzobiotics
Enzobiotic is a combination of synbiotics and proteolytic enzymes and is medically approved to improve protein metabolism, which can benefit people with CKD and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Enzobiotics work by improving the gut microbiota, which can help to reduce inflammation and improve protein metabolism. They reduce the levels of protein-bound uremic toxins (PBUTs) in patients with CKD. PBUTs are a group of toxins produced by the breakdown of proteins in the body. Supplements have below combination of bromelain, papain, pancreatin, trypsin and chymotrypsin as proteolytic enzymes.
B Vitamins: Folate, B6, and B12
B Vitamins play a vital role in managing Chronic Kidney Disease. High doses of B vitamins, specifically folate, B6, and B12 reduce plasma homocysteine levels. Moreover, high doses of these vitamins are more effective than standard doses in achieving these results, thereby potentially lowering cardiovascular risks for patients with Chronic Kidney Disease.
While high-dose B vitamins reduce homocysteine levels, their impact on mortality and cardiovascular issues is unknown. Additionally, CKD patients, especially those with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), should be cautious with cyanocobalamin, a form of B12. Alternatives like hydroxocobalamin or methylcobalamin are preferred due to better safety for managing Chronic Kidney Disease.
Vitamin D3
Vitamin D3 helps in CKD by maintaining calcium and phosphate balance, reducing inflammation, and managing secondary hyperparathyroidism. This supports bone health, lowers cardiovascular disease risk, and improves overall quality of life for CKD patients.
Intravenous Iron
Iron deficiency is prevalent in end-stage renal disease (ESRD) due to factors like blood loss and reduced dietary intake. Intravenous iron supplementation is crucial for managing this deficiency and maintaining optimal haemoglobin levels. However, Proper administration guidelines must be followed to avoid iron overload, which often leads to adverse effects such as inflammation, cardiovascular disease, and increased infection risk due to high serum ferritin levels. Balancing iron supplementation helps prevent these complications, ensuring better health outcomes and quality of life for patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Alpha Lipoic Acid
Alpha lipoic acid is a powerful antioxidant that helps reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which are significant contributors to CKD progression. Its antioxidant properties also protect kidney cells from damage and improve metabolic functions.
Sodium Bicarbonate
Sodium bicarbonate helps to neutralize excess acid in the blood, addressing metabolic acidosis frequently seen in CKD patients. Correcting acidosis slows the progression of kidney disease, improves muscle function, and enhances the overall quality of life.
Proteins and Amino Acids
Adequate protein intake is essential for maintaining muscle mass and overall health. In CKD, careful management of protein intake helps reduce the kidneys’ workload. Supplementing with essential amino acids provides necessary nutrients while limiting protein breakdown products that strain the kidneys.
Melatonin
Melatonin helps manage sleep issues in CKD by regulating the sleep-wake cycle. It improves sleep quality and duration, reduces insomnia, and alleviates sleep disturbances commonly experienced by CKD patients, enhancing their overall well-being and health
Niacinamide and Niacin
Niacinamide and niacin play a significant role in managing chronic kidney disease (CKD) by inhibiting phosphorus absorption, which is crucial for Chronic Kidney Disease patients who often struggle with elevated serum phosphorus levels. Furthermore, effective phosphorus management helps prevent complications like vascular calcification and bone disease. Additionally, adjusted doses of niacinamide highlight its potential for safe and effective use in children with CKD. Incorporating these supplements significantly improves mineral balance and overall health in CKD patients.
Zinc for Managing Chronic KidneyDisease
Zinc is an essential nutrient for managing chronic kidney disease (CKD), addressing several deficiency-related issues. CKD patients often experience zinc deficiency, leading to impaired taste, reduced appetite, pruritus, and decreased erythropoietin responsiveness. Zinc supplementation improves these symptoms, enhancing taste acuity, and appetite, and alleviating pruritus. Additionally, zinc boosts immune function contributing to overall better health.
Magnesium
Magnesium plays a crucial role in managing chronic kidney disease (CKD), particularly in balancing serum levels. In non-dialysis CKD patients, hypermagnesemia is a concern, while dialysis often leads to significant magnesium losses. Hence, proper magnesium supplementation helps address these imbalances. Magnesium supplementation slows arterial calcification and improves markers of atherosclerosis, which are critical for cardiovascular health in CKD patients. Therefore, maintaining appropriate magnesium levels through supplements is essential for preventing complications and promoting better cardiovascular outcomes in individuals with CKD.
Vitamin K
Vitamin K plays a crucial role in vascular health. Many hemodialysis patients have low levels of Vitamin K, which is concerning since this vitamin is vital for preventing vascular calcification. Vascular calcification leads to severe cardiovascular issues, a common complication in CKD. Supplementing with Vitamin K helps maintain adequate levels, potentially reducing the risk of calcification and promoting overall cardiovascular health. Ensuring sufficient Vitamin K intake through supplements is therefore essential for mitigating vascular complications and improving the quality of life for CKD patient
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is essential for managing chronic kidney disease (CKD) due to its antioxidant properties. CKD patients often experience Vitamin C deficiency because of dietary restrictions and losses during dialysis. Supplementation helps address this deficiency, supporting immune function and overall health. However, it’s crucial to balance the dosage carefully; excessive Vitamin C can lead to hyperoxalemia and increased oxidative stress, potentially harming kidney function. Properly managed Vitamin C supplementation ensures CKD patients receive the benefits without the risks, aiding in the maintenance of health and potentially improving outcomes in those undergoing dialysis
N-acetylcysteine (NAC)
N-acetylcysteine (NAC) is a valuable supplement for managing chronic kidney disease (CKD) due to its antioxidant properties. It reduces oxidative stress, which is crucial for CKD patients, decreases the incidence of cardiac events and improves renal function. Additionally, NAC offers specific benefits for dialysis patients by effectively treating hemodialysis-associated pseudoporphyria. These combined effects make NAC an important supplement for enhancing overall health and managing complications associated with CKD, particularly in reducing cardiovascular risks and improving kidney health.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is essential for managing chronic kidney disease (CKD) due to its role in mitigating oxidative stress. It offers potential cardiovascular benefits and helps improve conditions like erythropoietin resistance, muscle cramps, and restless legs syndrome, common in CKD patients. Furthermore, supplementation with mixed tocopherols is recommended for safety and efficacy, ensuring comprehensive antioxidant protection. By addressing oxidative stress and associated symptoms, Vitamin E contributes to better overall health and quality of life for CKD patients.
Vitamin A For Managing Chronic Kidney Disease
Vitamin A supports CKD management by promoting immune function, maintaining vision, and aiding in cellular growth. It helps prevent infections, a common issue in CKD patients and supports skin and mucous membrane health, contributing to overall well-being.
Fatty Acids
Fatty acids help in relieving symptoms of Chronic Kidney Disease and improving overall health. Supplements like evening primrose oil and fish oil effectively alleviate pruritus, a common and distressing symptom in CKD patients. Moreover, omega-3 supplementation, found in fish oil, offers additional benefits, including reducing graft failure and alleviating depression symptoms. Furthermore, by providing relief from itching, promoting cardiovascular health, and supporting mental well-being, fatty acid supplements are essential components of CKD management, enhancing patients’ quality of life and helping to prevent complications associated with the condition.
Selenium
Selenium supplements are key in managing Chronic Kidney Disease due to their impact on immune and cardiovascular health. CKD patients often have selenium deficiencies, which affects thyroid function. Supplementing with selenium helps support the immune system and cardiovascular function. However, it’s essential to ensure optimal dosage and consider safety, especially in CKD patients, to prevent adverse effects and maintain overall health while managing the condition
Curcumin For Managing Chronic Kidney Disease
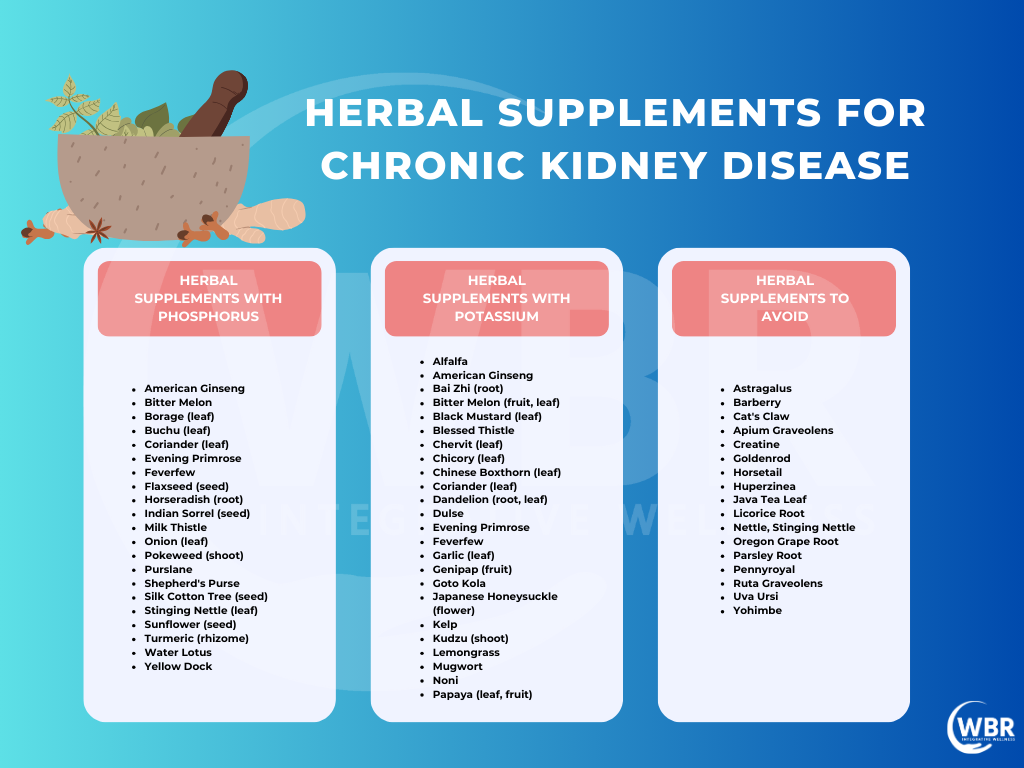
Curcumin is an anti-inflammatory compound that helps alleviate CKD symptoms. Some doctors recommend it despite limited evidence, as it could offer symptom relief. However, curcumin supplements often contain high potassium levels that are harmful, especially in advanced CKD. Using a highly bioavailable form, like Meriva phytosome complex, is advisable to maximize benefits while minimizing risk.
Coenzyme Q10 for Managing Chronic Kidney Disease
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) supplements play a vital role in managing chronic kidney disease (CKD) by potentially improving cardiac function and slowing cardiovascular disease progression. Moreover, CoQ10’s antioxidant properties and potential benefits for heart health make it a valuable supplement in the management of CKD, particularly for supporting cardiovascular function.
Lead Exposure and Chelation Therapy for Chronic Kidney Disease
Lead exposure poses a significant risk to kidney disease progression, even at low levels. EDTA chelation therapy improves renal function; however, its administration requires careful consideration due to potential side effects. While chelation therapy may offer benefits, it’s crucial to weigh the risks and benefits and administer it under close supervision to manage chronic kidney disease effectively
L-carnitine for Managing Chronic Kidney Disease
L-carnitine helps CKD patients by enabling the body to utilize fats for energy, improving anaemia, and clearing acyl CoA toxins. Deficiency of this vital nutrient leads to depression, fatigue, and cognitive issues. Regular blood tests should monitor L-carnitine levels for Chronic Kidney Disease patients. If deficient, start with 500-1500 mg per day, adjusting based on blood work results, to enhance energy, mood, and overall quality of life
Capsaicin Cream for Pruritus in Chronic Kidney Disease
Capsaicin cream is a promising option for managing pruritus, particularly in hemodialysis patients. Its topical application has shown effectiveness in relieving itching associated with dialysis. However, caution must be exercised in its use. Proper handling and application techniques are crucial to avoid adverse effects such as burning sensations or skin irritation. When used correctly, capsaicin cream becomes a valuable tool in alleviating the discomfort of pruritus in individuals with chronic kidney diseases.
Prebiotics and Probiotics Therapy for Managing Chronic Kidney Disease
Probiotics and prebiotics are quite beneficial in managing chronic kidney disease (CKD). They help balance gut microbiota, reducing uremic toxins and inflammation associated with CKD. Probiotics introduce beneficial bacteria, while prebiotics feed these bacteria, enhancing gut health. Improved gut health positively impacts overall health and slows down CKD progression, making these supplements a valuable addition to the management strategy for CKD patients. Acacia Fiber is one of the most crucial probiotics for Chronic Kidney Disease patients.
Thiamine for Managing Chronic kidney Disease
Thiamine (vitamin B1) is essential for patients undergoing dialysis, as they are at a high risk of deficiency due to dietary restrictions and dialysis-related losses. Thiamine deficiency leads to serious neurological conditions, such as Wernicke’s encephalopathy, characterized by confusion, lack of muscle coordination, and vision problems. Supplementing with intravenous thiamine shows positive outcomes in dialysis patients, effectively preventing these severe complications. By ensuring adequate thiamine levels, patients will be able to maintain better neurological health and overall well-being, making thiamine supplementation a critical component in the management of chronic kidney disease (CKD)
Key Nutritional Guidelines and Dosage for Managing Chronic Kidney Disease
- Take 1 to 2 multivitamin pills daily with food. ( preferably non sodium, potassium and phosphorus based)
- Consume Fish Oil containing EPA 1500-3000 mg and DHA 1000-2000 mg per day, divided into two or three doses with food.
- If needed, take 2,000-5,000 IU of Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol) once daily with food.
- If required, start with 325-650 mg of Sodium Bicarbonate per day between meals or on an empty stomach.
- Take 300-500 billion CFUs of probiotics daily, either between meals or with food. Ensure the product includes Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactibacillus plantarum and Bifidobacterium longum, with additional strains acceptable.
- “Probiotic Loading”: For the first 30 to 40 days, take 300-600 billion or more CFUs daily to rapidly repopulate gut bacteria.
- Take 200-400 mg of CoQ10 once or twice daily with food.
- Consume 30-70 grams of Acacia Fiber (Acacia Gum) daily, divided into two or three doses with or without food, with higher doses preferred
- Enzobiotics 4-6 capsule which is combination of synbiotics and proteolytic enzymes (Bromelain, papain, pancreatin, trypsin and chymotrypsin)
- L-carnitine 1-2 grams based on albumin level and weakness.
- Amino acids with 9 essential aminos 3-6 grams based on total protein and albumin level
Conclusion
Managing CKD effectively requires a multifaceted approach, including the use of key nutritional supplements. Each supplement discussed here offers specific benefits that help mitigate symptoms and improve the quality of life for CKD patients. However, supplementation should always be tailored to individual needs and monitored by healthcare professionals to ensure safety and efficacy. Ongoing research and personalized treatment plans are essential to optimize the health outcomes for those living with CKD.









