Functional Medicine Approach to IgA Nephropathy
Imagine waking up every morning with blood in your urine, high blood pressure and visible swelling in the hands and feet. This is how a normal day in the life of people suffering from IgA Nephropathy feels like. This condition, also known as Berger’s disease, silently affects kidney function and necessitates a profound understanding.
IgA Nephropathy is the result of the immune system’s misguided targeting of the kidneys, resulting in inflammation and potential long-term complications. A condition of such complexity warrants a comprehensive and professional approach.
Functional Medicine is a beacon of hope in this journey towards renal health. In this blog, we embark on a journey to understand the paramount role of Functional Medicine in managing IgA Nephropathy. This approach goes beyond symptom management, aiming to uncover the fundamental causes, and offering tailored solutions that resonate with each individual. So let us explore the functional medicine approach to IgA Nephropathy.
What is IgA Nephropathy?
IgA Nephropathy, sometimes referred to as Berger’s disease, is an autoimmune kidney condition which is the result of an unusual immunological reaction. The body makes IgA and other types of antibodies to help fight off invading pathogens (i.e. bacteria, viruses) and prevent disease. It is one of the first lines of defence against invading organisms from the environment, diet, and toxins. In this disorder, an excessive amount of IgA antibodies build up in the kidneys, eventually causing inflammation and damage. The primary location of this accumulation in the kidneys is in the glomeruli, which are small filtering organelles. It frequently shows up as microscopic or extensive hematuria (blood in the urine). Furthermore, long-term progression leads to renal problems that are more serious. Understanding this condition is essential because it informs treatment plans that include changing one’s lifestyle, dietary modifications, and increasingly using a functional medicine approach that takes a holistic perspective.
Causes and risk factors
A number of causes and risk factors lead to this renal disorder.
Genetic Predisposition: Genetic components are important. An increased risk exists in people with a family history of IgA nephropathy. There is a link between greater vulnerability to this illness and specific gene variations.
Immunological System Dysfunction: One of the main causes is an aberrant immunological response. In this disorder, the immune system goes awry, resulting in an overabundance of IgA antibodies building up in the kidneys. Kidney injury and inflammation are brought on by this.
Environmental Factors: While the immune system and genetics are the main contributors, environmental factors also play a role. IgA Nephropathy occasionally occurs before or is brought on by infections, especially respiratory or gastrointestinal illnesses. Toxin exposure and dietary variables also play an important role such as heavy metal cadmium in IgA nephropathy case.
Leaky GUT: Imbalance of microbes in the gastrointestinal tract (may be something infectious like clostridia, yeast overgrowth, a parasite, h.pylori or simply an insufficiency of or imbalance in good gut bacteria). One of the major drivers for dysbiosis is antibiotic use, especially multiple extended courses over time. But medications, toxins, stress, food choices, low Vitamin D, and many other factors may be involved.
Food sensitivities: Food triggers are very often involved in autoimmune activation and exacerbation. Gluten, dairy, lectins and soy are the most common triggers. IgG antibodies are only one type of reaction that the body can have to a perceived threat (e.g. a food) while IgA-mediated response (which happens in the mucous membranes of the body, such as the gut lining).
Understanding these causes and risk factors helps in managing and potentially preventing IgA Nephropathy, especially in individuals with a family history or known genetic predisposition.
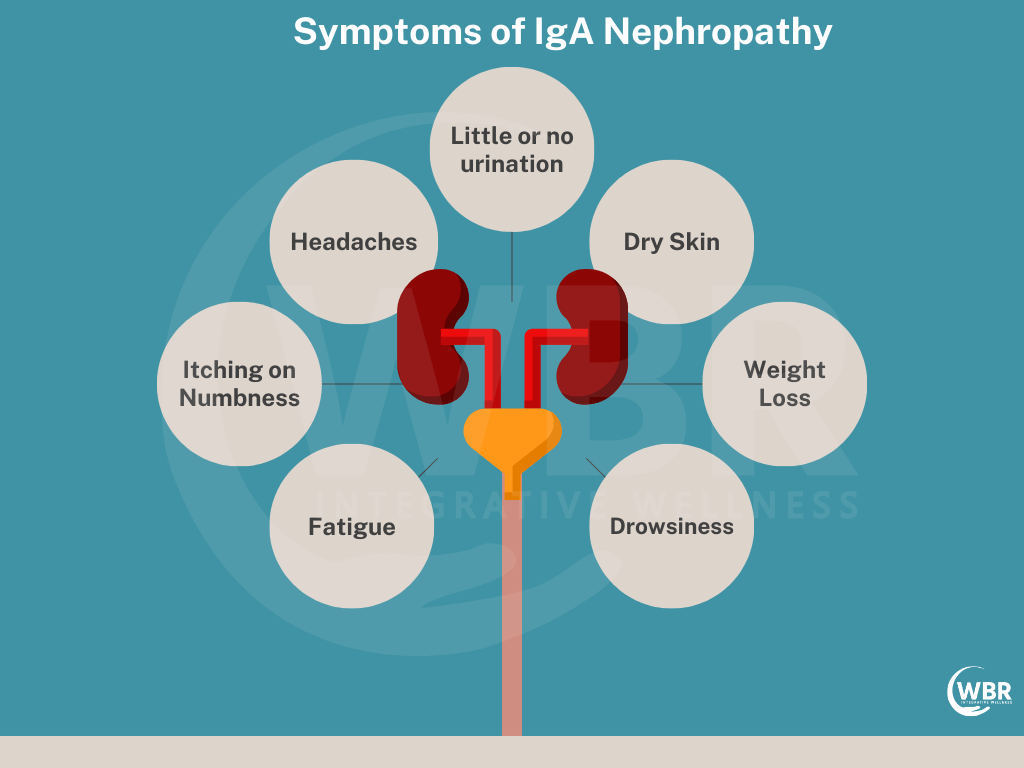
Triggers of IgA Nephropathy
Many triggers and factors lead to this chronic renal disorder. Understanding these triggers is crucial for managing the condition effectively. Hence, let us look at some of these common triggers.
Infections and Their Role: Infections, particularly respiratory and gastrointestinal infections, are primary triggers for IgA Nephropathy. These infections provoke an abnormal immune response, leading to the accumulation of IgA antibodies in the kidneys and subsequent inflammation.
Dietary Factors: Although the exact dietary triggers are not fully elucidated, research suggests that dietary components, including high red meat consumption and excessive salt intake, play a role in IgA Nephropathy. Diets low in fruits and vegetables have also been examined as a root trigger leading to IgA Nephropathy. Furthermore, food allergies also trigger IgA Nephropathy. The combination of food antigens and IgA antibody lead to renal issues.
Lifestyle Factors: Lifestyle choices such as smoking and heavy alcohol consumption sometimes contribute to overall inflammation and immune system dysfunction, potentially worsening IgA Nephropathy.
Stress and Its Impact: Chronic stress, while not a direct cause, weakens the immune system and exacerbates inflammation. Stress management strategies are crucial for individuals with IgA Nephropathy to help mitigate its effects.
Functional Medicine Approach
Genetic Testing: Functional medicine begins with genetic testing to identify any predispositions or genetic factors that might influence the development or progression of IgA Nephropathy. This information guides personalized treatment plans.
Immune System Evaluation: A comprehensive assessment of the immune system is crucial. Functional medicine practitioners analyze immune function to understand the specific immune responses contributing to IgA Nephropathy and to tailor interventions accordingly.
Gut Health Analysis: Since the gut and immune system are closely interconnected, evaluating gut health is essential. Dysbiosis or gut inflammation impact IgA production and immune responses, making gut health optimization a key component.
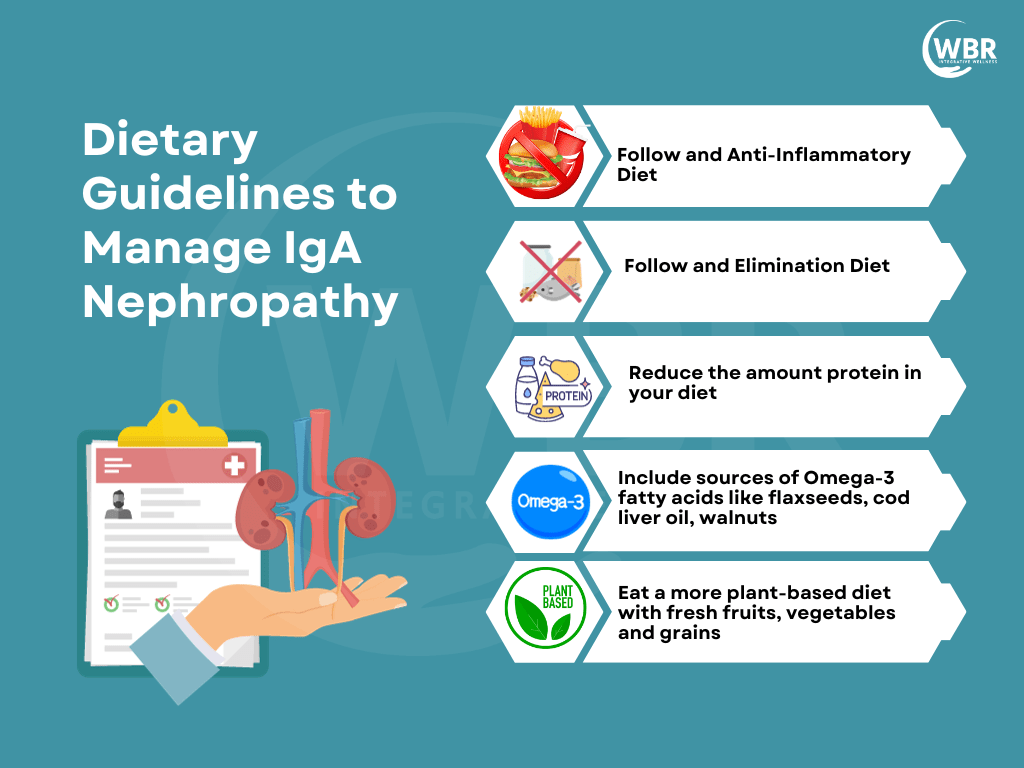
Dietary Modifications: Functional medicine prescribes personalized dietary changes to reduce inflammation and support kidney health. Avoid eating gluten entirely (even if it’s not on her sensitivity list). In some people, gluten can promote increased intestinal permeability through increased secretion of a protein called zonulin. Also to reduce phosphorus, sodium, limiting protein, and increasing the consumption of anti-inflammatory foods and following an elimination diet. One must start with an elimination diet in the first few weeks and then follow an anti-inflammatory diet for the long run. Furthermore, research shows that a gluten-free diet helps in managing IgA Nephropathy. Additionally, a diet rich in prebiotics and dietary fibers help manage conditions like IgA Nephropathy. Certain probiotic strains like Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG and L.Plantarum also help manage such conditions.
Nutritional Supplements: Targeted supplementation with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants help address deficiencies and support kidney function. These supplements are selected based on individual needs.
Lifestyle Changes: Functional medicine emphasizes lifestyle modifications, including smoking cessation, alcohol moderation, and regular exercise to reduce overall inflammation and improve well-being.
Stress Management Techniques: Stress can exacerbate IgA Nephropathy. Functional medicine incorporates stress-reduction strategies such as meditation, mindfulness, and relaxation techniques into the treatment plan.
Collaboration with Various Healthcare Professionals: Functional medicine takes a collaborative approach, involving nephrologists, dietitians, mental health professionals, and other specialists to provide holistic care and address all aspects of the condition.
Monitoring and Adjustments: Regular monitoring of kidney function and overall health is essential. Functional medicine practitioners continuously assess progress and make adjustments to the treatment plan as needed.
This comprehensive Functional Medicine Approach aims to address the root causes of IgA Nephropathy, provide personalized care, and empower individuals to take an active role in managing their condition for improved kidney health and overall well-being.
Supplements
Omega-3: The Omega-3 Fatty Acids present in fish oil have a positive effect on the patients suffering from IgA nephropathy due to its anti-inflammatory properties. Dose of total EPA and DHA around 4-5 grams split into 2-3 dose where EPA to DHA ratio is 2:1
Phytosome Curcumin: Herbal anti-inflammatory herb, especially curcumin ( meriva form) which has bio-availability of 10 times more than plain curcumin.
Vitamin E: Vitamin E also plays a crucial role in fighting various autoimmune disorders. It works by stabilizing cell membranes and lysosomal membranes.
Wormwood: Artemisia Absinthium which is commonly called absinthe or wormwood has exhibited a significant reduction in proteinuria and arterial blood pressure in the early stages of IgA.
Probiotics: Probiotics strains such as B.longum, L. acidophilus, L.paracasei HEAL, L.plantarum (299v), B. Coagulan GBI-30, 6086, Rhamnosus GG, L.Reuteri, L. Gasseri (BNR17), B.Infantis and L.fermentum can be very helpful to reduce the inflammation and uremic toxins load.
Prebiotics: Prebiotics fiber such as acacia fiber, PHGG (partially hydrolysed gaur gum) helps in optimising butyrate levels as it support microbial rebalancing.
Thunder god vine: It is used as a dietary supplement for autoimmune diseases and has shown tremendous benefits for IgA nephropathy. It has shown that it can lower proteinuria, reduce inflammation and many cases went into remission.
Mucilaginous herbs: L-glutamine, N-acetyl-glucosamine, MSM, DGL, slippery elm, marshmallow, chamomile, okra extract, cat’s claw and quercetin, helps in healing and nourishing the intestinal lining in order to ensure optimal nutrient absorption and prevent autoimmune reactions.
Other Supplements: Vitamin D3,K2, Vitamin B complex, Vitamin C ( Ester form), L-Carnitine, Coenzymes Q10, SPMs can be very complimentary in reducing inflammations.
Conclusion
The Functional Medicine approach to IgA Nephropathy offers a promising paradigm shift in the management of this complex kidney disorder. By delving into the root causes, focusing on personalized treatment plans, and promoting holistic wellness, Functional Medicine empowers patients to take an active role in their healing journey. This approach recognises that IgA Nephropathy is not a one-size-fits-all condition, and tailors interventions to each individual’s unique needs. While conventional medicine often primarily treats symptoms, Functional Medicine aims to address the underlying imbalances contributing to the disease. Combining the best of modern science with a patient-centred, holistic perspective, it offers hope for better outcomes and improved quality of life for those living with IgA Nephropathy.