Celiac Disease: Chronic Digestive Disorder
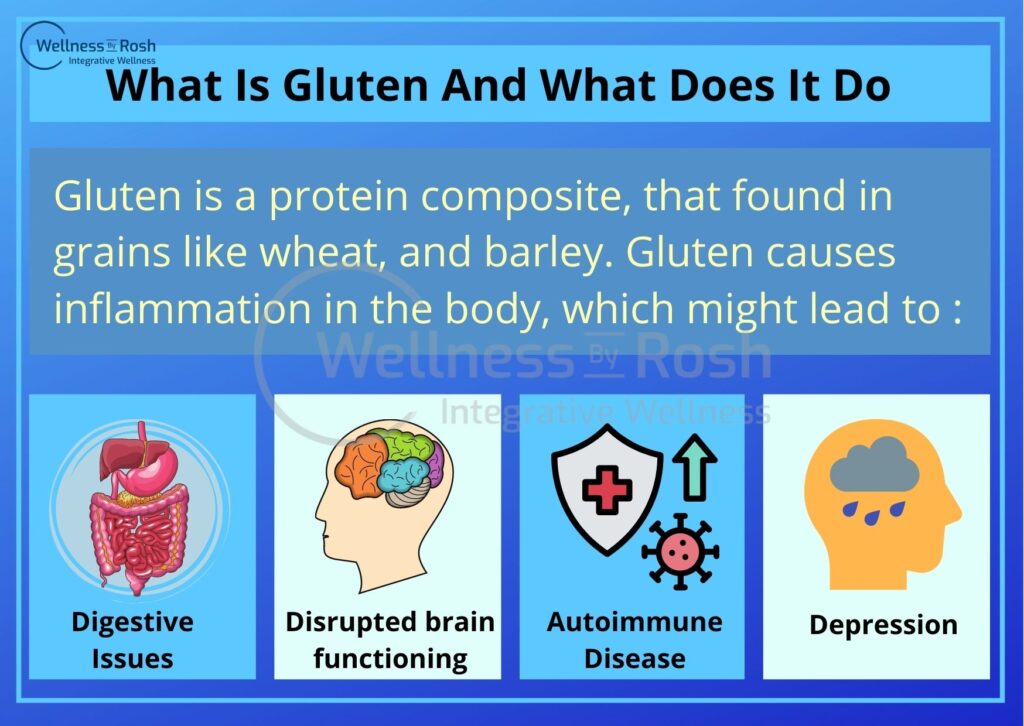
Celiac disease is a serious autoimmune condition, triggered by the consumption of a protein called gluten. Gluten is mainly found in bread, pasta, and any other food containing grains like wheat, barley and rye. The gluten allergy causes inflammation and damage to the lining of the small intestine, and make it nearly impossible to absorb certain nutrients.
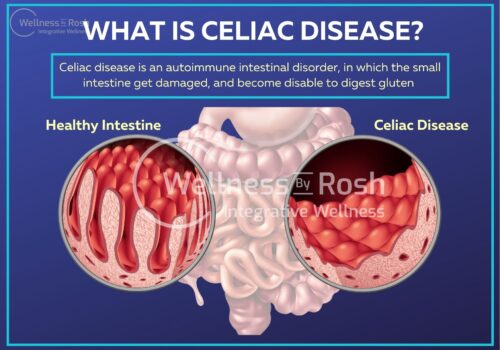
What Is Celiac Disease
Celiac disease (also known as celiac sprue or gluten sensitive enteropathy) is an autoimmune disorder in which the consumption of gluten triggers the body to attack itself. It is a multisystem disorder that means it may affect several organs.
When a person with celiac disease consume gluten, it damages the small intestine’s fingerlike projections the villi as a result the nutrient absorption get affected badly and that can lead to indigestion and other serious health issues such as bone fractures, bacterial, viral and parasitic infections etc.
Who Gets Celiac Disease?
According to the Celiac Disease Foundation, about 1 in every 100 people is a affected by celiac disease. unfortunately many people living with this condition remain undiagnosed or misdiagnosed. Celiac disease is a genetic condition it mean this passes from one generation to other via DNA. It has been seen that some stressful events like, pregnancy, surgery, infections and emotional distress can induce the disease.
Celiac Disease And Gluten Intolerance Are the Same?
Though celiac disease may look same as gluten intolerance or wheat allergy, but they are not the same conditions. The difference between these two conditions is in the immune system, Celiac disease is an autoimmune condition, means, the immune system attacks its own tissues as if it were an invader. On the other hand, in gluten tolerance or wheat allergy only some temporary effects such as bloating and other gastrointestinal distress has been seen, no long term harm to the body.
What Causes Celiac Disease?
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder, that means consuming gluten can induce the disease.
Other factors also trigger the development of celiac disease. Some major factors are:
- Genetic Predisposition- Those with celiac conditions have a particular gene (HLA DQ2 and HLA DQ8 genes).
- Imbalance of Gut Microbiome
- Environmental Factors– Surgery, pregnancy, Childbirth, Infant feeding.
- Processed Food and Additives
- Intestinal Permeability
- Infections and Pathogens
- Chronic Stress
- Immune System Distress- Bacterial, Viral and Parasitical Infections.
- Food Intolerance
Common Symptoms Of Celiac Disease
Unfortunately Celiac disease, some time remain undiagnosed because its signs and symptoms are not specific. The symptoms range from mild to severe and different in children and adults. The symptoms can be within the digestive system and can be outside the digestive system as well.
Symptoms Within Digestive System
- Abdominal pain
- Abdominal swelling
- Bloating and Gas
- Constipation
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
Symptoms Outside The Digestive System
- Headache
- Anemia
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Fatigue
- Mouth Ulcers
- Unexplanatory Weight loss
- Joint pain
- Chronic Eczema
- Malabsorption
- Dermatitis herpetiformis (Skin rashes)
Complications Of Celiac Disease
If untreated for a long period, celiac disease may leave a person vulnerable and can lead to affect many other organs. Some health complications may include:
- Malnutrition
- Infertility
- Intestinal Cancer (very rare)
- Osteoporosis– low bone density
- Delayed puberty in children
- Food Intolerance (lactose)
- Pancreatic disease
- Neurological problems- ADHD, epilepsy, headache and migraine
A Person who has celiac disease may prone to develop other autoimmune diseases in the near future, including:
- Thyroid Disorder
- Type-1 Diabetes
- Lupus
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Autoimmune liver disease
- Kidney disease (nephrosis)
Types Of Celiac Disease
There are various kind of celiac disease. These include:
- Classic Celiac Disease- Inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Neoclassic Celiac Disease- Without GI symptoms but other health problems.
- Silent Celiac Disease- No symptoms but immune protein present in the blood and damage the small intestine lining.
- Latent Celiac Disease- Positive with celiac disorder but no damage to the small intestine villi.
- Refractory Celiac Disease- Severely damaged intestine because of chronic inflammation of the GI tract and increased risk of liver cancer.
Diagnosis Of Celiac Disease
Recognizing celiac condition might be difficult because its symptoms can be confused with other IBS (irritable bowel syndrome), still as health care providers became more aware, they suggests to perform two simple tests to diagnose celiac disease.
-
Blood Test
- Genetic test of HLA-DQ8 and HLA-DQ 2.2
- Antibodies anti-transglutaminase type 2 antibody (anti-TG2) and anti-endomysium antibodies (EMA).
- Organic acid test (urine) such as d-lactate, arabinitol, benzoate, phenylacetate, p-hydroxy-benzoate, indican, p-hydroxy-phenyl-acetate
It is important that before being tested, the patient fed with the gluten rich diet such as bread, pasta etc. Because consuming gluten free diet before the test, may impact the result and show a false negative result.
-
Endoscopy
During the endoscopy, the doctor inserts a thin hollow tube (endoscope) through the mouth and check for the damage of the small intestinal lining (villi), takes a sample for further examination. To avoid any kind of discomfort during the procedure, endoscopy is done with anaesthesia.
Disease Management
Though there is no specific medications or surgeries are available that can cure the autoimmune disease, however on-time detection and strategic management can prevent severe complications in near future. You can manage the severity of this disease by adopting some lifestyle and diet changes.
Lifestyle Changes
- Try to be stress free- as stress triggers all kinds of autoimmune conditions. Practice some kind of meditation and yoga asanas to reduce your stress level.
- Try to get community support- as we earlier discussed most of the time the disease remain undiagnosed, it is a good idea to connect with other people with the same symptoms and guide each other.
- Be open about your condition- It is natural and understandable if this disease makes you physically and emotionally drained, share your feelings with your health coach, so that they can suggest you what best suits in your food habits and lifestyle.
Dietary Changes
- A completely gluten free diet is the best prevention for this disease. With the celiac disease condition, it becomes very crucial to know which food is completely gluten free in the real sense.
- Make a habit to read the ingredient label thoroughly because sometimes gluten free food is not 100% gluten free, there is some amount of gluten is present in any level.
- Prefer eating home cooked food is the best way to completely avoid gluten in your diet.
- Avoid consuming too many processed gluten-free foods, because processed food may be high in chemicals, sugar and unhealthy fats that might can trigger the celiac disease.
- If the symptoms remain unchanged even after following a strict gluten-free diet, A person may also consider some different diet such as:
- Dairy-Free Diet
- Elimination Diet
- Anti-inflammatory Diet
- Try to include Probiotic in your diet- as probiotic will improve the gut- microbiome.
- Daily intake of plenty of various fiber (preferably soluble) and prebiotics supplements (pectin, FOS).
- Chew your foods thoroughly to improve the intake of nutrients.
Key Nutritional support
- High dose of EPA to reduce intestine inflammation
- Glutathione, L-glutamine to repair GI tract
- Yeast-free probiotic strains both bifidobacterium and lactobacillus such as L. Reuteri, B. Longum, L. Gasseri, B. Caugulans, B. Infantis etc
- B complex supplements with the right constitution of B12, B9, B6, and B1
- A raw food-grade iron supplement might be needed as deficient
- L-carnitine and alpha-lipoic acid for energy and adrenal
- Vitamin K (MK7) as deficient because of CD
- Magnesium 400-500 mg to maintain the normal pH
- Zinc 50-80 mg daily to support immunity and healing
- Prebiotic fibers such as acacia Senegal, FOS, inulin, guar gum support the microbiome for healing.
What Food To Include And Eliminate, If You Are Having Celiac Disease
For Celiac Disease condition, it is important to know what not to eat (gluten-free food), but the major question arises what we should eat actually. If you are also facing this kind of dilemma, no worries anymore, here we are going to solve your confusion.
Pantry Suggestions For Celiac Disease
Here is the list of food, commonly recommended for the person to manage the symptoms:
- Naturally gluten-free grains, like rice, quinoa and millet
- Nuts and seeds
- Beans and lentils
- Whole fruits and vegetables
- Healthy cooking and baking oils
- Nutritional yeast
- Spices like cinnamon, ginger, and turmeric
- Some herb like oregano, thyme, and parsley
Food To Avoid In Celiac Condition
- Barley
- Bread
- Cake
- Crackers
- Ice-cream cones
- Muffins
- Noodles
- Soy sauce
- Teriyaki sauce
- Wheat flour
- All-purpose flour
SOME FAQ
- Undiagnosed celiac disease can also result in malabsorption of B12, B9, and low B6
- Any child who is not thriving, not able to gain weight, or having skin issues like blisters and sores could have Celiac disease.
- Vitamin K deficiency caused by CD can lead to a lack of clotting factor.
- Many patients with celiac disease have ADHD symptoms that improve with a GF diet.
- Gene HLA DQ2 and HLA DQ8 reside within the HLA gene group and are known risks for developing celiac disease.
- Gluten-free diets are shown to improve psoriasis severity only in those with known celiac disease.
- Read all labels carefully and watch out for hidden sources of gluten.
- Celiac is often difficult to diagnose because of overlapping symptoms with IBS, Crohn’s, Anemia, Ulcers, etc.
Conclusion
Living a healthy life with the celiac disease condition is not impossible, you can manage the disease easily by completely removing the gluten from your diet. To treat your symptoms, it is very important to understand your condition because you may get confused with the wheat allergy, celiac disease and Non celiac gluten allergy as the symptoms are almost same. But the good news is with the proper recommendations you can easily manage this condition and live a normal life.










How to manage Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) naturally. - Wellness By Rosh | Integrative Wellness
27-Apr-22[…] loose. this may lead to various autoimmune conditions including asthma, Rheumatoid arthritis, celiac disease, lupus, ulcerative colitis […]
Functional Medicine Approach For Ulcerative Colitis - Wellness By Rosh | Integrative Wellness
2-Aug-24[…] food allergens might trigger or exacerbate symptoms. Common allergens include cow’s milk, wheat, eggs, corn, and citrus fruits. Furthermore, avoidance of these foods often leads to remission or […]