How to manage Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) naturally.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a chronic relapsing disease that affect a major population worldwide. It may affects a person’s daily life and can cause abdominal pain, cramping, diarrhoea, painful bowel movement, excess bloating and other digestive problems. There are many multifactorial reason including stress, genetics, leaky gut, celiac disease, SIBO, food sensitivities, visceral hypersensitivity, enteric infection, neuroendocrine dysfunction, and inflammation that play a major role to trigger the IBS condition.
In this blog, we will explain what is IBS, what are the possible causes, signs & symptoms, and how can we naturally manage this triad of abdominal discomfort using Integrative approach.
What Is Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) also known as spastic colon or irritable colon, can happen to anyone at any age but it is commonly seen in young adults, and mostly in middle-aged women. IBS is a long-lasting condition that is not life-threatening but definitely affects your quality of life. In this condition, the Gastrointestinal tract is troubled with significant symptoms such as poor bowel habits, abdominal cramps, bloating, constipation, visceral hypersensitivity, pain, diarrhea, and changes in stool appearance, etc.
IBS represents an imbalance within the digestive system. We must evaluate beyond suppression-based treatment to understand the underlying cause of imbalance in the area of nutrition, gut flora, immune system, emotional health and environment.
Types Of IBS
Broadly Irritable bowel conditions can be grouped into mainly 3 categories, depending on the type of stomach motility and bowel movement such as constipation-predominant, diarrhoea-predominant, and mixed.
1. IBS-C
IBS-C (Constipation dominant IBS) is a condition raised by chronic constipation with abdominal pain. Approximately one-third worldwide population is affected by IBS-C.
2. IBS-D
IBS-D (Diarrhoea dominant IBS) is a condition characterized by frequent diarrhoea with abdominal pain.
3. IBS-M
IBS-M (Mixed IBS) is the condition when the affected person experiences an alternating pattern of constipation and diarrhoea.
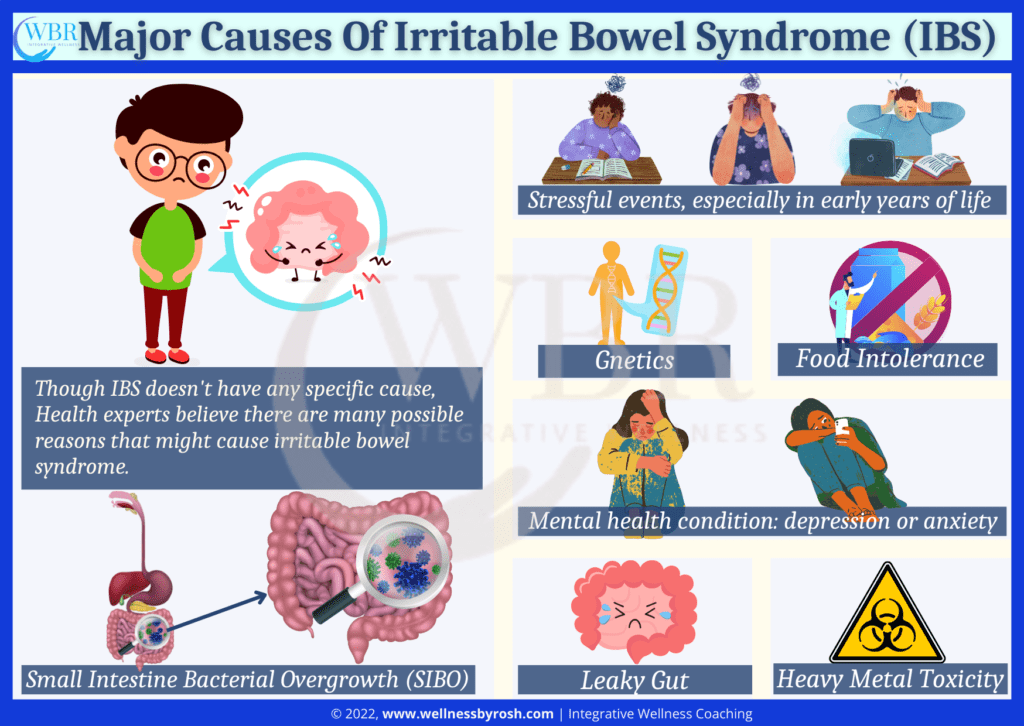
What Are The Possible Cause Of IBS
Since what exactly causes the IBS is not known, small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), leaky gut, food intolerance and stress are the factors that play an important role to trigger the IBS condition.
-
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO)
SIBO or small intestinal bacterial overgrowth is the condition when bacteria present in the gut migrate and populate the small intestine, which may cause gas & bloating, and other discomforts due to the fermentation of digested food in the wrong place of the gastrointestinal tract.
-
Leaky Gut
A leaky gut occurs when the food particles start passing through the gut linings because the intestinal junction becomes loose. this may lead to various autoimmune conditions including asthma, Rheumatoid arthritis, celiac disease, lupus, ulcerative colitis etc.
-
Heavy Metal Toxicity
Environmental toxins such as some medications, certain food, polluted air, water and soil can enter the body through ingestion or inhalation and impair the body’s normal functioning including bowel movement. An excess amount of several heavy metals like mercury, arsenic, cadmium and chromium can lead to toxicity.
-
Food Intolerance
People with irritable bowel syndrome often have a food intolerance or food sensitivities. Food intolerance means when your body shows an immune-mediated response to a certain food, the immune system produces antibodies against that food. It s very common.
You must have heard about lactose intolerance where a person can not digest milk or any dairy product, that is an example of food intolerance or food sensitivity. Gluten, dairy, corn, nuts, eggs and soy are the common food that shows intolerance in some people.
-
Chronic Stress
Stress plays a crucial role in the development of IBS symptoms. Studies show that psychological and physical stress causes bowel dysfunction and impaired the gut microbiome and increases intestinal permeability, which leads to IBS.
-
Genetics
Researchers claimed that the person with IBS condition has a specific genetic defect, that affects the bowel movement and causes IBS.
-
Mental Health
Certain mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety are associated with IBS.
-
Gut-Brain Interference
The gut is considered the second brain of the body. The brain is connected to the gut through various nerves and IBS creates impairment in that connection which may lead to other digestive issues such as abdominal pain, constipation and diarrhoea.
What Are The Common Signs And Symptoms Of IBS
The symptoms of irritable bowel may differ in each person, some common signs and symptoms of IBS include:
- Frequent Gas & Bloating
- Abdominal Discomforts: stomach pain, cramp
- Nausea
- Constipation
- Diarrhoea
- Constipation Altering With Diarrhoea
- Mucus In The Stool
- Stress
- Anxiety and Depression
- Frequent Urination
- Heartburn And Indigestion
- Headache
- Food Sensitivity
- Tiredness
Diagnosis Of IBS
There is no specific test to diagnose IBS, your health care provider may suggest you perform some tests to rule out any other serious conditions like celiac disease, colon cancer or IBD. These tests include:
- Lactulose Test: for Leaky Gut
- Microbiome Testing: To check the composition and diversity of microorganisms present in the gut.
- SIBO Test: Hydrogen breath testing (for lactose or glucose)
- Fecal elastase: for the pancreatic enzyme.
- Fecal calprotectin: to check inflammation in the stool.
- Motility Test: for muscle activity in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Secretory Protein: to check digestive immunity.
- CRP (C-reactor protein): to check the inflammation of the body
The above mentioned test can be extremely helpful which can vary from case to case based on past health history and current sign & symptoms.
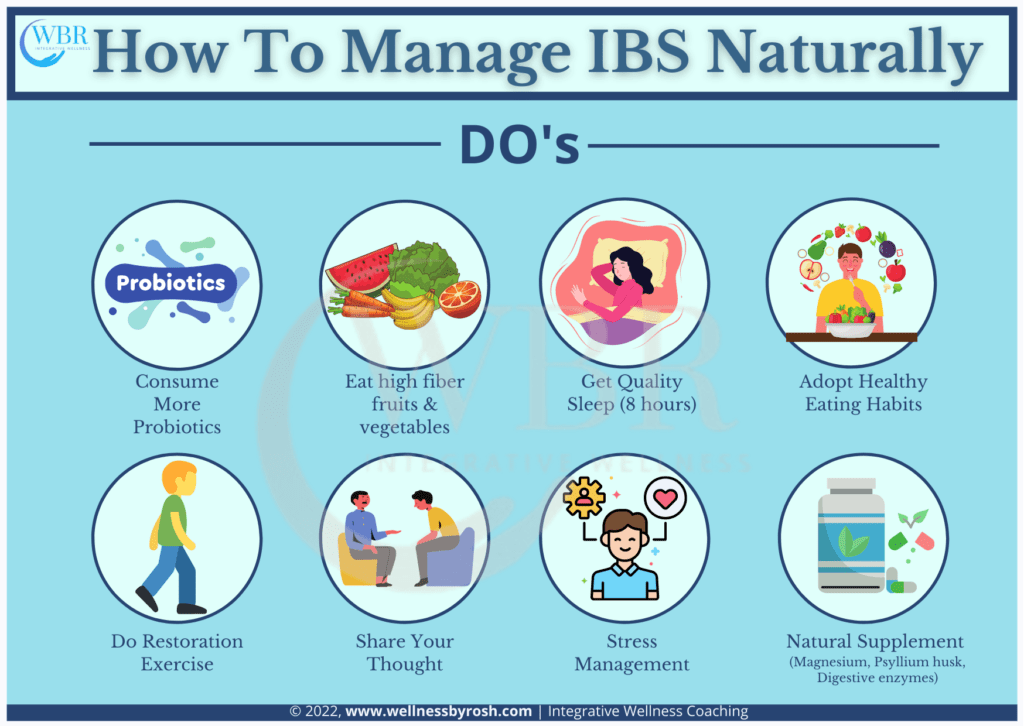
How To Naturally Reverse And Manage Irritable Bowel Syndrome
The IBS treatment needs to be a personalised treatment because every person is unique in their condition and there are one-size-fits-all reversing strategies. However right diagnosis and strategic management can prevent severe discomfort in long run. You can manage the symptoms by adopting some diet and lifestyle changes.
We recommend the following strategies to manage the IBS condition:
- Lifestyle Improvements
- Dietary Modifications
1. Lifestyle Improvements
Lifestyle changes help to improve symptoms over time. Some lifestyle changes are:
-
Manage Your Stress Level
Stress is the major trigger of IBS condition, whether it is psychological stress, mental or physical. Managing stress levels is the most important thing to starting your IBS reversal journey.
-
Make Sure You Are Getting Quality Sleep
Getting at least 7-8 hours of good sleep may help in bowel movements.
-
Practice Restorative Workouts
An Intense workout doesn’t help in IBS, some calming practices such as Yoga, meditation, stretching and walking, support manage the IBS
-
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
It is a psychological therapy, that focuses on the link between feelings, thoughts and behaviour. In short, it is a talk therapy session to ease your mind’s stress level.
-
Share Your Thought
Sometimes talking to someone is work as a therapy session. IBS causes mood swings, anxiety and depression, talking and sharing your thoughts with someone can be extremely helpful.
2. Dietary Modifications
Some diet modifications might ease the IBS symptoms.
-
Choose High Fiber Snacks
Almond, popcorn, pears, and strawberries are high fiber foods that may help to ease constipation. You can also try fiber supplements if the fiber food is not solving the problem.
-
Wisely Choose Your Green
If you are experiencing excess bloating and gas problems, stop using cruciferous vegetables like cauliflower, cabbage, broccoli and brussels sprouts etc.
-
Practise Healthy Eating Habits
Always choose fresh and organic fruits, vegetables, whole grains food over fried, packet food and fast food.
-
Keep a Journal
Keep a journal about what you are feeding to your body because IBS is unpredictable, by this way you will find out your trigger food items.
-
Some Diet Protocols That May Help
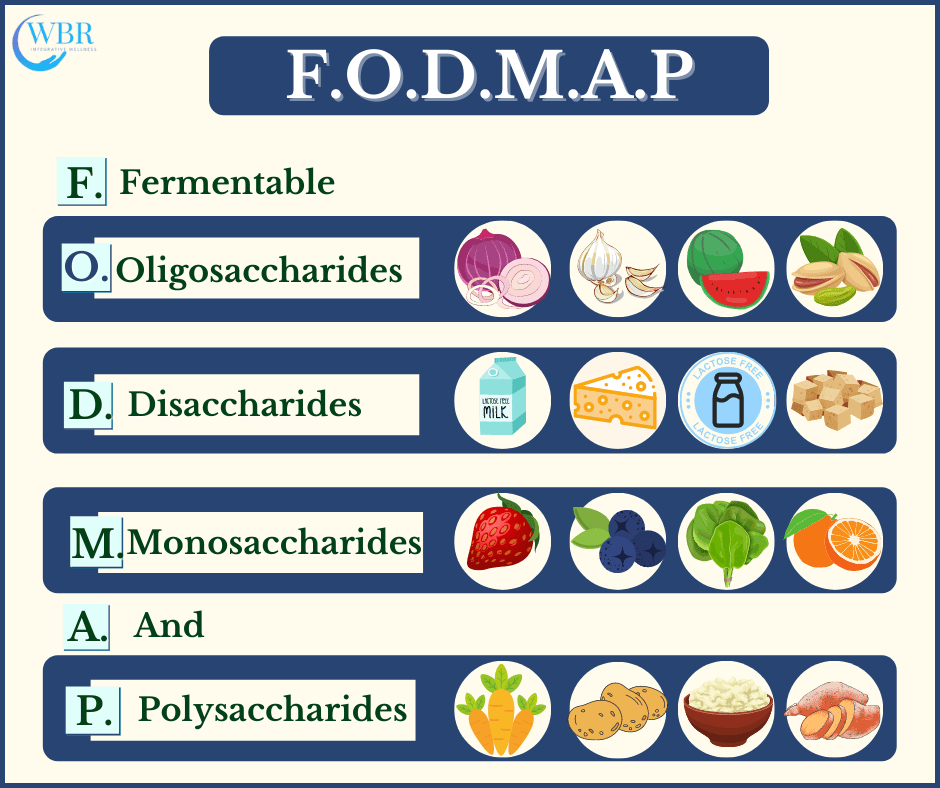
Ayurvedic, gluten and grain-free, dairy-free, Microbiome, low fodmaps, elimination diet are considered the best diet that helps in managing IBS.
Key Nutritional Support
- Berberine helps in reducing inflammation in the GI tract. Help in managing IBS-D symptoms.
- Probiotics help in the growth of good bacteria in the gut. Probiotics may be an effective way to manage symptoms of IBS-C, IBS-D, and IBS-M. Strains like L. Brevis, L. Plantarum, B, Infantis and L. Reuteri are very effective.
- Prebiotics soluble form such as FOS, apple pectin, gaur gum, acacia senegal and inulin.
- Magnesium citrate works as a natural laxative for constipation (IBS-C).
- Peppermint Oil shows anti-inflammatory properties and provides relief for abdominal pain, bloating and gas.
- Saccharomyces boulardii supplementation can help in reducing diarrhea and in stool formation (IBS-D).
- L-Glutamine is the most essential amino acid for the gut. It helps in maintaining the intestinal lining.
- Vitamin D3 supplement to maintain optimal level.
- B12 and B complex for proper muscle tone in the gastrointestinal tract.
Note: Kindly consult with your medical practitioners before starting any supplementation.
Recommended Food
-
- Healthy Fats: Avocado, coconut oil, olive oil, walnut oil etc.
- Stocks: Vegetable stock
- Low-FODMAP fruits and Vegetables
- Herbs: Basil, thyme and rosemary
- Grains: Rice and quinoa
Food To Avoid In IBS Condition
-
- Grains and gluten
- Dairy: Milk, butter, cottage cheese etc
- Processed food: Chips, packets and canned food items
- Trans fat: Deep-fried food
- Beverages: Coffee, alcohol
Conclusion
IBS is a common gastrointestinal condition that can affect anyone at any stage of life. It is crucial to identify underlying root causes that develop the IBS symptoms. Natural remedies, diet and lifestyle changes help a lot to heal the gut and provide relives to abdominal discomforts.
The first step toward reversing/managing the disease is becoming aware of all the potential symptoms and possible causes of IBS. then next step would be adopting a integrative nutrition and lifestyle that support the healing of the gut and would not lead to any serious health hazards to the body.