Cooking Oil: Healthy Vs Unhealthy
Nowadays, supermarkets are flooded with many types of cooking oils. Bringing the right kind of cooking oil among several options is a task. Different cooking oils are used for specific purposes. Some oils are good for deep frying, some are good to use as it is drizzling or garnishing purposes. This blog will definitely help you to choose the right oil for you and your family.
What Is Cooking Oil And How Are They Produced?
Basically cooking oils are the fats, that is extracted from different plants, nuts, and seeds. Since our body requires a variety of healthy fats, it is crucial to know about the different types of fat present in different oils.
The reason for the various type of oil present in the market is, they are extracted from mainly two techniques,
“Cold-pressing” (extracted without any heat, eg: extra virgin olive oil),
“Hot-pressing” (extracted with heat and pressure) and
“Refined oil“, (extracted using solvent, refining, bleaching and deodorising process.
Coldpress and Hotpress are nutritionally better but expensive, however, Refined oil is pocket friendly but compromise the quality and flavour.
Types Of Fats Present In Oils
It is crucial to know a bit about fat if you want to understand cooking oils. Fats are basically of three types:
- Saturated fats: are solid at room temperature. Stable and resist oxidation. eg. Coconut oil.
- Polyunsaturated Fats: are liquid at room temperature, easily oxidize, not good for cooking. eg, Sunflower oil
- Monounsaturated Fats: are also liquid at room temperature, they are more stable and resist oxidation. eg. canola oil, and nuts oil.
How To Store Oil In Right Way
When it comes to the stockpiling of oil, you need to be very careful, some oils become rancid if exposed to light, heat and oxygen (especially polyunsaturated oils).
If you want to preserve the nutritional integrity of the oil, always store it in a cool, dry and dark place, consume it within 12 months of its manufacturing date. Remember, oils are not a wine, the older, the better; instead Oil loses its flavour and quality with time.
Points To Be Taken Care While Using Oils
All oils will lose their benefits over time, however, there are many ways we can store the oil in the right way and minimize the deterioration.
- Avoid store-up oil- Be extra careful on noticing the manufacture date and consume the oil within 12 months.
- Store it in a cool & dark place- Store the oil in a dark glass bottle and keep it in a dry, dark place.
- Don’t overheat oil while cooking- Avoid heating oil to its smoking point, as it produces some unwanted chemicals that damage the oil.
- Don’t reuse heated oil- Oil once heated, loses its flavour, do not use the same oil again and again as it becomes rancid.
- For high flame cooking, use the right oil
- Always use organic Ghee that is made using the traditional hand churning, Bilona method, and Organic Oils, which is extracted from the cold-press technique.
- Don’t overdue as oils have high omega-6 like 3-4 teaspoons a day.
- Adjust your omega-3 ratio to maintain a good balance of omega3:omega-6 ratio for optimal health.
What Is The Smoke Point Of The Oil?
A temperature at which, oil starts to smoke up and start burning is called the smoke point of the oil. Overheating produces harmful chemicals, that damage the oil properties.

What Are The Best Oil For Cooking?
Here is our list of the healthiest cooking oils, which we can further divide into three main categories.
- Oils, best for High-Temperature cooking
- Oils for baking
- Oils for dressing and marinations
1. Oils, Best For High-Temperature Cooking
-
Ghee (Organic )
Ghee has been used in Indian cooking for ancient years. When clarified butter is cooked for a longer time, and evaporates more moisture, it turns into Ghee. This is the reason for its long shelf life. Just remember that the Ghee should be organic and made by the traditional hand churning, Bilona method.
Benefits: Ghee contains conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), a healthy polyunsaturated acid, vitamin A, E and K.
Best For: Because of its high smoking point, Ghee is ideal for pan-frying and cooking.
Smoke Point: 485°F
-
Peanut Oil
Peanut oil is commonly known as groundnut oil, traditionally used in Asian cooking. Almost half of the peanut oil is made up of monounsaturated fats.
Benefits: Peanut oil is a great source of vitamin E.
Best For: Grilling, roasting, and Deep frying.
Smoke Point: 450°F
Tip: Peanuts oil should not be consumed by those, who have any kind of allergy to peanuts.
-
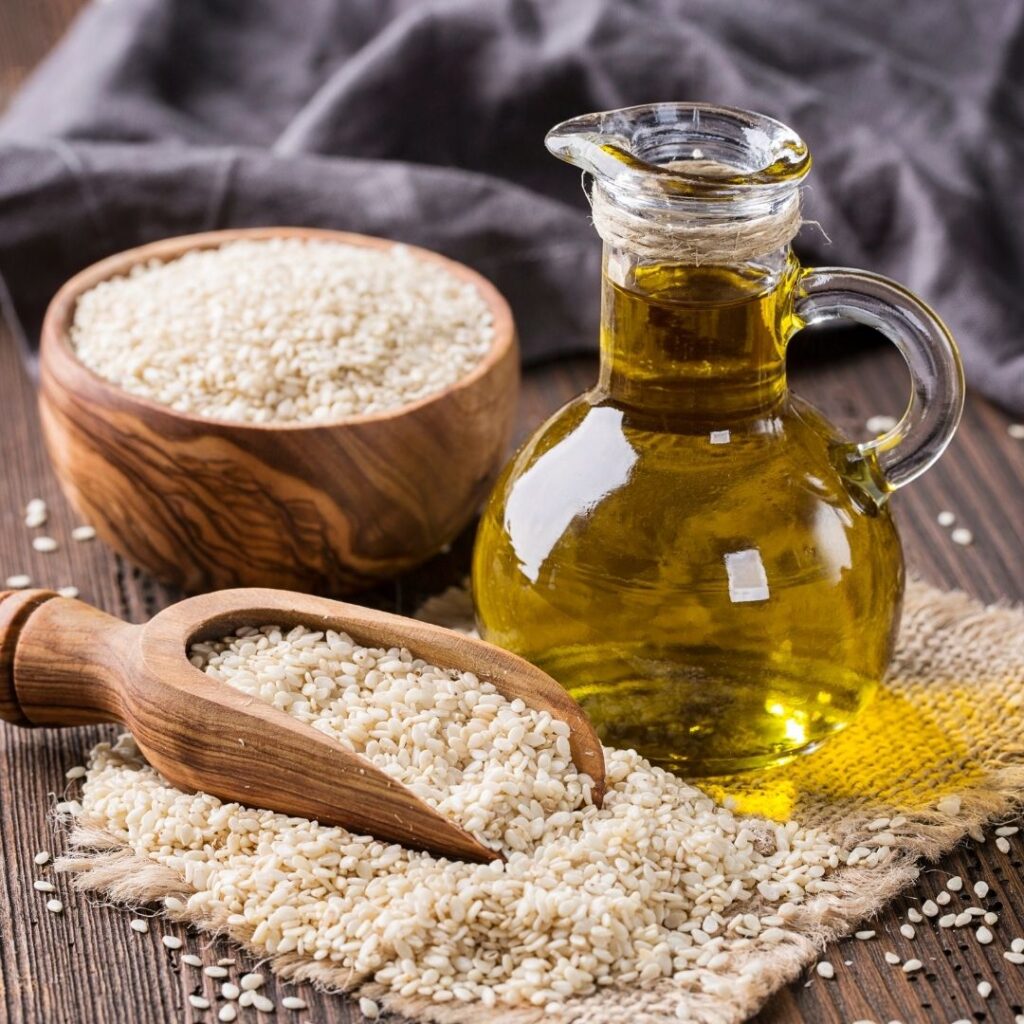
Sesame Oil
Sesame oil is high in both, mono and polyunsaturated fats. It is refined from raw or toasted seeds but the extraction process is the same as the cold-pressed technique.
Benefits:
- Sesame oil contains two powerful antioxidants; sesamol and sesamin.
- Daily consumption of sesame oil improves bone health.
- It is high in copper, zinc, magnesium and iron.
- Vitamin B is present in a high amount in sesame seeds.
- Reduces stretch marks to an extent.
Best For: Stir-frying, Deep frying and sauteing.
Smoke Point: 450°F


-
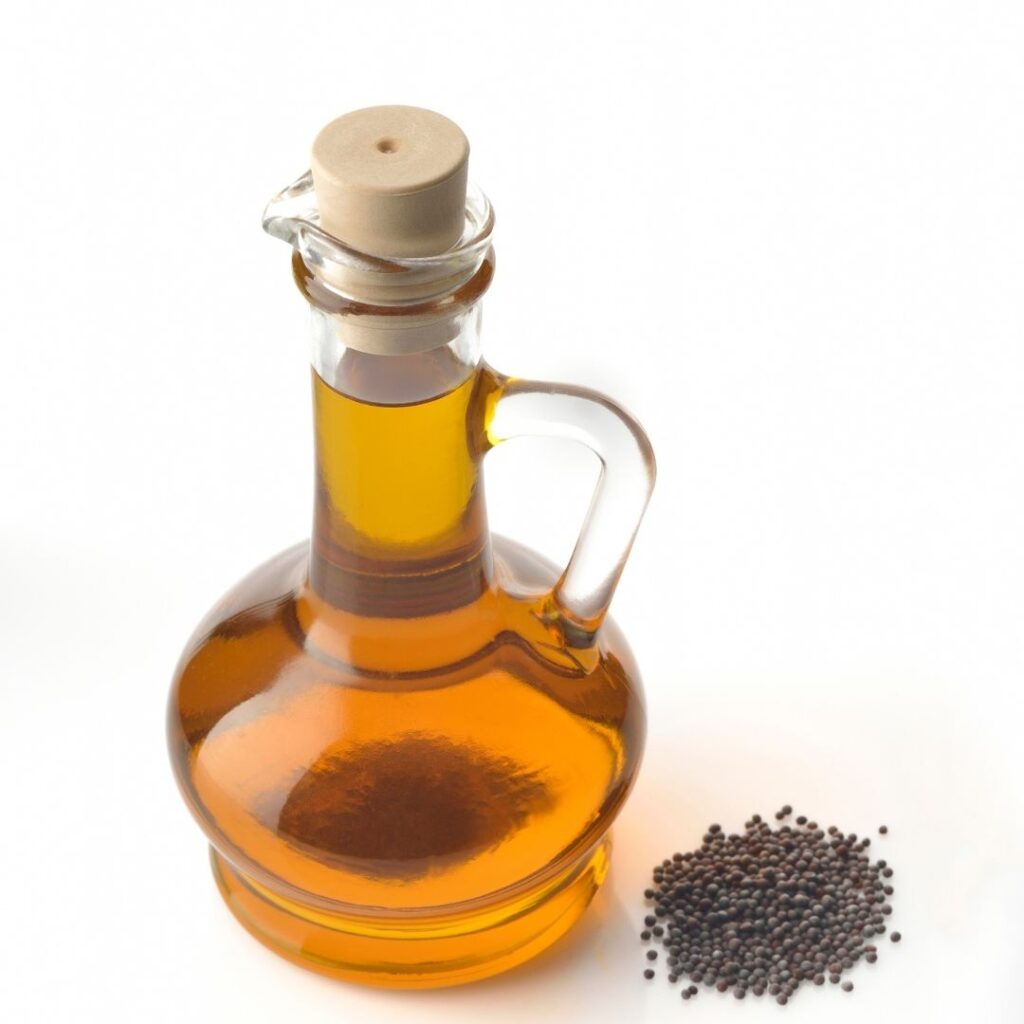
Mustard Oil
Pure mustard oil is made by pressing the mustard seeds. It is high in monounsaturated fatty acids and beneficial for cardiovascular health.
Benefits: Reduce inflammation and pain, good for skin and hair.
Best For: Deep frying, sauteing, pan-frying and roasting
Smoke point: 249°F
2. Oils For Baking
-
Coconut Oil
Coconut oil is solid at room temperature, as it is comprised of 90% saturated fats. There is a contradiction about the health benefits of coconut, according to some studies coconut oil increases the good HDL cholesterol, while some studies show it raises the bad cholesterol HDL.
It does not go well at a very high temperature.
Best For: Baking and sauteing
Smoke Point: 350°F (unrefined) and 450°F (refined)
-
Avocado Oil
Avocado oil is rich in healthy monounsaturated fats. It is made up of the flesh of pressed avocado. It has a versatile, mild flavour that goes with any kind of cooking.
Generally, it comes in a spray container so one can control the usage.
Best For: Baked goods, roasting, spraying.
Smoke Point: 375°F (Virgin), 520°F (refined)
3. Oils For Dressing And Marinations
-
Olive Oil
Olive oil is rich in healthy monounsaturated fatty acids. Especially the oil of unripe olives which undergo cold-pressed techniques, rich in antioxidants. It contains omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. It is not suitable for cooking it has a very low smoke point.
Benefits: Good for the heart, reduces the risk for cardiovascular disease and stroke. Increase metabolism and help in weight management.
Best For: Salad dressings and sauteing
Smoke Point: 375°F (Extra-virgin), 465°F (refined)
-
Flaxseed Oil
Flaxseed oil is rich in healthy omega-3 fatty acids. It helps in reducing blood pressure and managing good cholesterol levels. Flaxseed oil needs to be refrigerated as it can oxidize very easily and go rancid. It can spoil quickly so, it is suggested to store this oil in a dark bottle and keep it in the fridge after use.
Benefits: It is a high source of omega-3
Best For: Salad dressings and drizzling
Smoke Point: 225°F
-
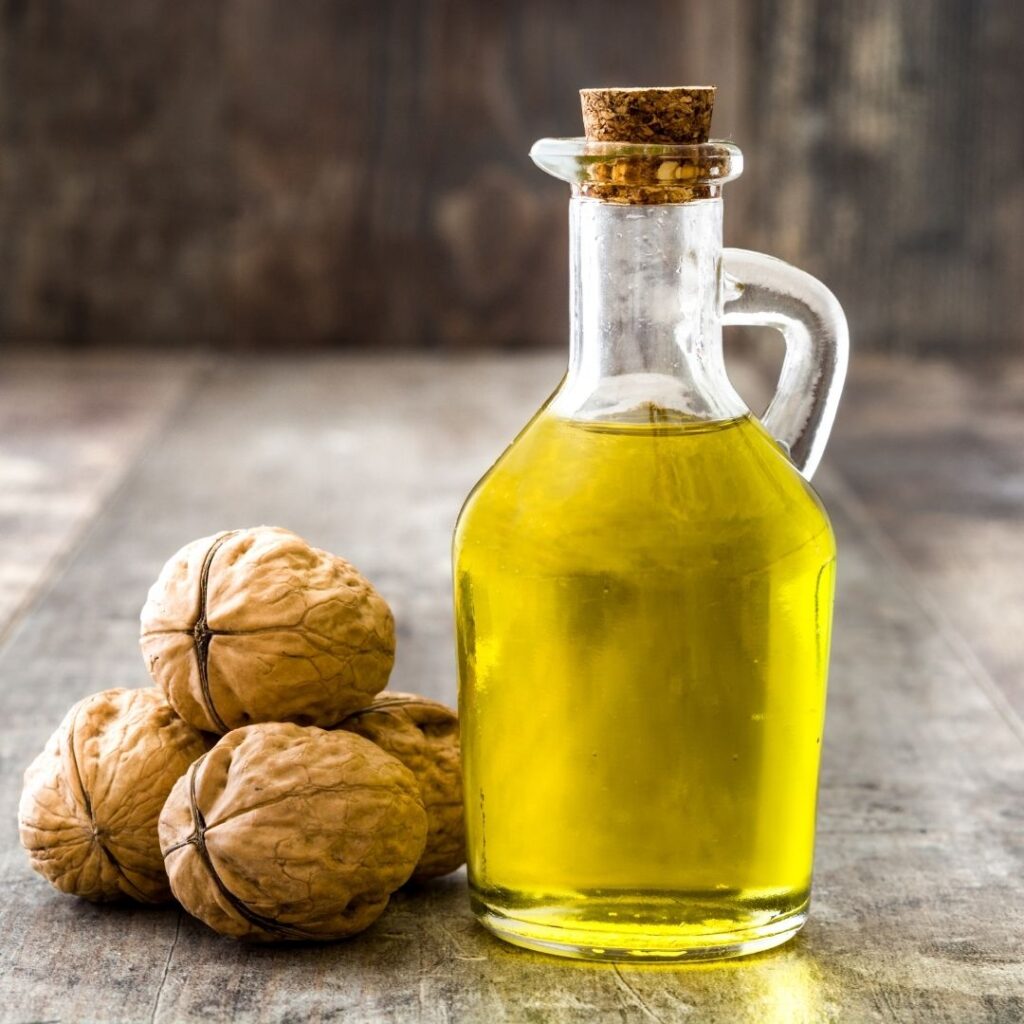
Walnut Oil
Walnut oil is a healthy oil, however, it has a low smoke point so, this oil is not good for cooking purposes. Since it goes rancid easily, it is suggested to store this oil in the fridge.
Benefits: It has a good ratio of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which helps to reduce inflammation.
Best For: Salad dressings and Drizzling
Smoke Point: 320°F

Some Oils Are Not Good For Cooking
- Some oils which extract from the seed on a large scale in industries are highly processed oil and are considered toxic seed oil.
- The process of extracting oil from the seeds takes place at a very high temperature to oxidize the fatty acids.
- The byproducts generate in this process are extremely harmful to our health.
- Some industrial toxic seed oils are:
- Canola oil
- Corn
- Cottonseed
- Soy
- Sunflower
- Safflower
- Grapeseed
- Rice bran oil
- Omega-6 are found in these industrial seed oils that can induce inflammation in the body.
Why Industrial Seed Oils Are Not Good For US
- Consuming industrial seed oil increases the omega-6 fatty acids in our bodies.
- Industrial seed oils are not stable and can be easily oxidized.
- When this oil is heated repeatedly ( in fryers), it produces even more toxic chemicals.
- The crops are genetically modified to produce more seeds that can increase oil production.
How are Industrial Seed Oils Affecting Our Health?
Industrial seed oils trigger many inflammatory diseases, some include:
- Asthma
- Autoimmune disease
- Cognitive & Mental Health
- Diabetes
- Gut related problems like IBS and IBD
- Inflammation
- Infertility
- Osteoarthritis

Conclusion
Which oil is suitable for you, depends on what kind of cooking you are doing in everyday life. The smoking point of the oil is also a thing to consider while choosing a good oil, some oils are healthy, but their smoke point is very low so, they can not be used for stir-frying or deep frying purposes.
Likewise, some oils are having a high smoke point cannot be used for dressing and drizzling purposes. The best source of poly and mono-unsaturated fats, that are good for the heart is the oil that is organic, comes from whole food and extracts from the cold-pressed technique. We recommend you keep all these points in mind and carefully choose your oil.









How To Develop Healthy Eating Habits In Kids - Wellness By Rosh | Integrative Wellness
18-Mar-22[…] children need healthy fats in their meals. Healthy fat help kid with bone density, skin, improves mood and help in […]
Daniella
26-Sep-24This article was such a fantastic find! The information is super helpful and perfect for anyone working on improving their health.
I really appreciate how you present everything in such a straightforward and useful way.
I’ll definitely be referencing this on my blog about wellness – my readers
will absolutely benefit from it. Thanks for putting this together