Omega-3 facts and health benefits
Omega-3 fatty acids are some of the most essential fatty acids you can feed to your body. These days you must have heard or read about omega-3 fatty acids, and their health benefits, many people use omega-3 supplements. well, what you have read or heard is true, omega-3 boosts your health in several ways. How? we will understand in this blog.
Fats & Fatty Acids Are Good or Bad!
Fats are used in many cuisines, especially in India it always consumed in an enormous amount in fried, fast food and everyday cooking.
It has always been criticized for so many right reasons, what if I tell you, not all fats are bad for the health, in-fact some good fats help to prevent lifestyle diseases.
Fatty acids are essential and a source of the energy, but it is important to know which type and what amount of fat should be consumed in day to day life.
Types of Fats/Fatty Acids
There are mainly 3 types of fats:
- Saturated Fatty acids
- Unsaturated Fatty Acids: are divided into 2 groups
- Monounsaturated Fatty acids: omega-9 fatty acids
- Poly Unsaturated Fatty acids: further divided into- omega-6 and omega-3
- Trans Fatty Acid
- While saturated and trans fatty acids are harmful to health, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids show a beneficial effect on your health.
- Among all the fatty acids (poly and monounsaturated fatty acids), only linoleic acid (LA), and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) are essential fatty acids (EFA) as these can not be synthesized by the human body.
- Linoleic acid (LA)commonly called Omega-6 and Alpha-linolenic fatty acid (ALA) commonly called Omega-3 fatty acid.
What Is Omega-3 Fatty Acid
Omegas are long-chain fatty acids, that plays an essential role in supporting the integrity of the tissues. since the body can not synthesize, it must out-source from the food, these kinds of fatty acids are called, essential fatty acids.
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fatty acids. There are three main types of Omega-3:
- Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) :
- Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA)
- Alpha-linolenic Acid (ALA)
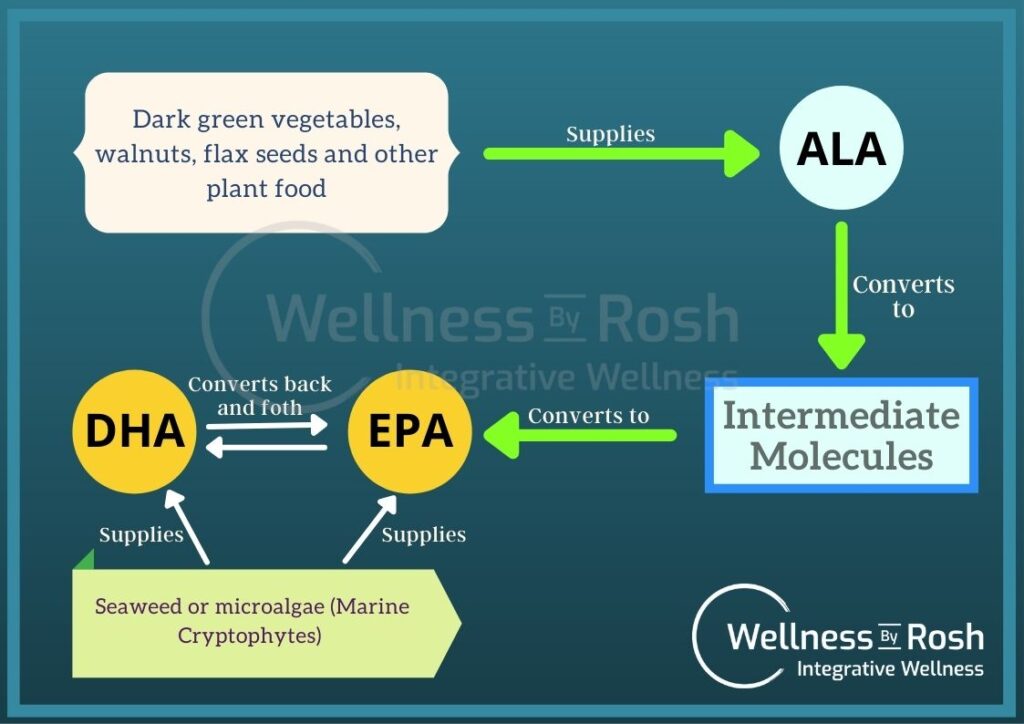
Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA)
- EPA is the marine form of omega-3, It is a polyunsaturated, essential fatty acid. This fatty acid is liquid at room temperature.
Source-
-
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) is mostly present in marine algae.
Functions-
-
- EPA is essential for the cardiovascular system and circulatory health
- It supports the body’s anti-inflammatory response since it works as an anti-inflammatory agent
Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA)
- DHA is a polyunsaturated fatty acid. It is also liquid at room temperature.
Source-
-
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), mostly present in Algae Oil (plant source).
Functions-
-
- DHA is essential for healthy heart function.
- DHA is extremely important for vision and brain cell development.
- DHA is vital for the nervous system proper functioning.
- It plays an important role in brain development, as half of the brain is made up of fats and most of this is DHA, an essential fatty acid.
Alpha-linolenic Acid (ALA)
- ALA is commonly known as vegetarian omega.
- ALA can be converted into EPA to an extent in the body.
Source-
-
- Flax seeds, chia seeds, walnuts, canola oil.
- Flax seeds are a source of omega-6, omega-3, linoleic acid and alpha-linolenic acid.
Sources of Omega-3
If you are a fish lover, you must have a sufficient amount of omega-3 in your body. Some good sources of omega-3 include:
- Algae oil
- Canola Oil
- Perilla Oil
- Chia seeds
- Flax seeds
- Walnuts
- Edamame
- Plant food: soya beans, hemp seeds, spinach, brussels sprouts.
- Dairy Products: from grass feed animals.
Some Facts
- Fish do not produce DHA and EPA, they get them from marine algae as their food. Therefore, the original producer of omega-3 (DHA & EPA) is marine algae (microalgae).
- Research shows that a high intake of omega-6 affects the omega-3 in the body. So, to increase the omega-3 fatty acid, eat more omega-3 rich food and limit the omega-6 rich food such as sunflower oil, corn, soybean oil, and cottonseed oil are rich in omega-6.
- The optimal ratio of omega-6: omega-3 is 2:1 or 1:1 while the western diet has a 20:1 to 15:1 ratio.
- ALA-rich oil or supplements doesn’t substitute for fish oils as only 2-10% of ALA is converted into EPA and DHA.
- Algae-based supplements mostly have DHA and no EPA.
- Krill oil is incorporated into phospholipids so has increased bio-individuality in spite of lower actual EPA and DHA.
- Fish oils are significantly safe as per studies even if you are on aspirin and have no bleeding risks on the dosage of 2-2.5 grams per day, however, if one has bleeding disorder then recommended to consume under medical supervision.
- Eating too much fish for an ideal omega-3 daily dosage is an issue because of mercury content.
- Fish oils appear to be safe during pregnancy at dietary doses of up to 2.5 grams of EPA and 100-300 mg of DHA daily.
Science-Based Benefits Of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 have been shown some powerful health benefits, some including:
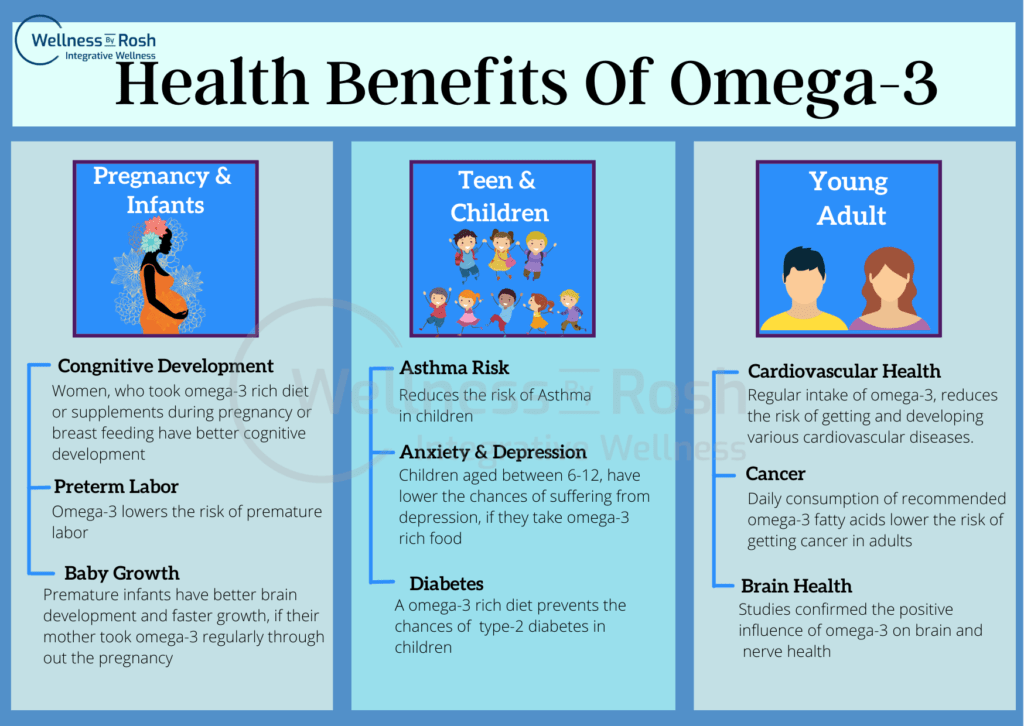
- Fight with anxiety and depression
- It plays an important role to improve vision and eye health
- Promotes brain health during pregnancy and in infants
- Support heart health and cardiovascular system of the body
- Reduce symptoms of “Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)” in children
- Help in reducing the symptoms of metabolic health
- It helps in reducing inflammation
- Omega-3 can fight autoimmune diseases including type-1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, lupus, psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis etc.
- It improves mental health
- It may help prevent cancer
- It may reduce asthma in kids
- Good for skin health
- Improves sleep quality
- Good for bones and joint’s health
- It may reduce fat from the liver (fatty liver)
- It helps in lowering the menstrual pain
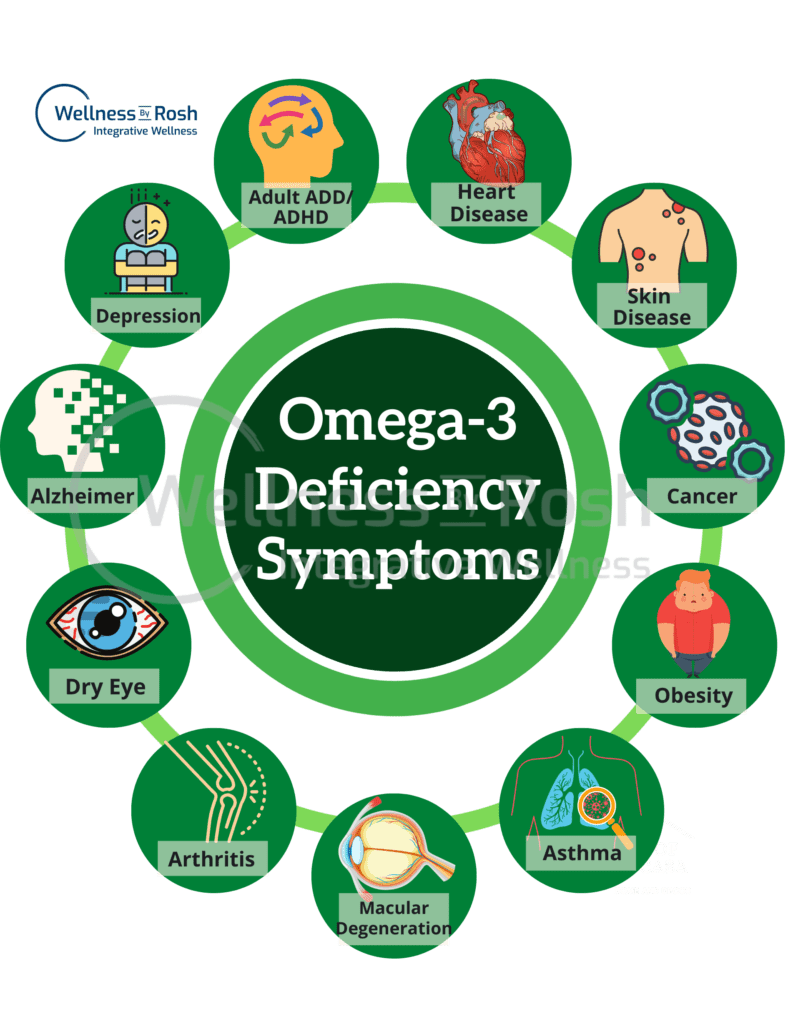
Deficiency of Omega-3
Deficiency of omega-3 may lead to several health issues, some including:
- Depression and anxiety
- Obesity
- Asthma
- Cancer
- Arthritis
- Alzheimer
- ADHA in children
- Skin Diseases
- Cardiovascular Diseases
Supplements Guidelines
Regular consumption of fish oil as supplements may reduce cardiovascular risks, and are beneficial in dementia, depression, diabetes, autism, cancer, asthma, hypertension, atopic dermatitis, rheumatoid arthritis, pregnancy, weight reduction, mental stress, anger, and anxiety.
- For a healthy adult, the daily recommended dosage is 2400 to 3600 mg combination of EPA and DHA (Omega-3) split over 2-3 times.
- Fish oil is the ideal form while buying the omega-3 supplement, carefully see the EPA and DHA content and check for third-party testing for mercury toxicity.
- Vegans can look into algae-based supplements which have both DHA and EPA.
- Certain health conditions such as autism, atopic dermatitis, hypertension, cancer may need a high dosage of up to 6000 mg daily.
Summary
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for good health. But is true that there no sufficient options are there through diet so it advisable to consider taking omega-3 supplement for immense health benefits.
To know more about supplements as per your age, gender, and requirement, it is always suggested to talk to your medical practioners , who can guide you in a better way.









Role of SPMs in Reducing Pain and Inflammation - Wellness By Rosh | Integrative Wellness
3-Sep-22[…] receptors to induce cell-type specific responses. They are derived from Arachidonic acid and Omega-3 fatty acids. Arachidonic acid is well known for its pro-inflammatory metabolite of the Omega 6 fatty acid. […]